Introduction to machining isn’t complete without the milling operation. No project runs smoothly without these vital steps. Whether you're making simple parts or building a complex part, knowing the milling process is vital. In this article, we will breaks down 12 different types of milling operations. Each method supports different design needs. Gain clarity and confidence in your machining workflow.

CNC Milling
CNC milling is a precise and flexible production technique to fabricate fine-quality products. It involves rotating cutting tools operating on a workpiece to shave off material through milling. The tools permit users to perform different processing operations after customization. A computer system controls all the movement operations of the machine activities. The ability to operate with such high precision helps create high-quality manufactured components.
A rotating cutter installed on the machine performs material shaping operations. Through control mechanisms, users can determine the depth and angle of the cutting process. The cutting tool defines the capability for moving through multiple pathways to generate complex shapes.
Milling operations vary greatly. The operational effectiveness depends on selected tools and materials. Surface grinding is considered the simplest operation in the milling process. When creating intricate products, complex mechanical movement is required to obtain the desired designs. Choosing the right operation demands a proper comprehension of available options.
Milling operations fulfill different objectives in the manufacturing process. The suitable operation depends on whether you need flat surfaces, angled cuts, or groove formations. The choice of materials you handle determines which milling operation yields the best results. Different milling operations are used for different projects. We should examine these operations to find the right one.
Table: 12 Common Types of Milling Operations
| Operation Type | Purpose | Characteristics | Best Use For |
| Face Milling | Cut flat surfaces | Perpendicular cutter, high-speed material removal | Finishing large, flat areas |
| Plain Milling | Remove material from flat surfaces | Horizontal cutter, basic surface prep | Surface leveling and clean-up |
| Side Milling | Cut vertical sides or grooves | Edge-based cutting with vertical surfaces | Grooves, slots, and edge shaping |
| Straddle Milling | Mill two parallel sides at once | Dual cutters on a single arbor | Machining symmetrical parts |
| Gang Milling | Machine multiple features simultaneously | Multiple cutters on one arbor | High-speed production of complex parts |
| Angle Milling | Create angled cuts or slots | The tool is angled relative to the surface | Chamfers, angled features |
| Form Milling | Cut unique or curved shapes | Custom-shaped cutter follows complex profiles | Gears, cams, and turbine blades |
| End Milling | Versatile cutting in vertical/horizontal axes | Cuts slots, pockets, and contours | General-purpose intricate machining |
| Saw Milling | Cut long slots or divide materials | Saw-like cutter for deep, straight cuts | Parting off large stock pieces |
| Gear Milling | Machine gear teeth are accurately | Special gear cutters for precise spacing | Gears of all types |
| Thread Milling | Cut internal or external threads | Spiral toolpath without tapping | Threading large or hard-to-machine parts |
| CAM Milling | CNC-controlled precision milling | CAD/CAM driven for complex geometries | High-accuracy, automated part production |
Let’s elaborate on above mentioned different types of milling operations;
In their operation, a cutting tool performs cuts directly on workpiece surfaces. The tool rotates perpendicular direction to the workpiece. It helps you create flat surfaces successfully. Most operations that need polished surfaces of large flat workpieces depend on this method.
The fast removal of bulk volumes is possible through face milling. It helps manufacturers meet all specifications or measurements with ease. Face milling helps keep complex parts smooth and even.
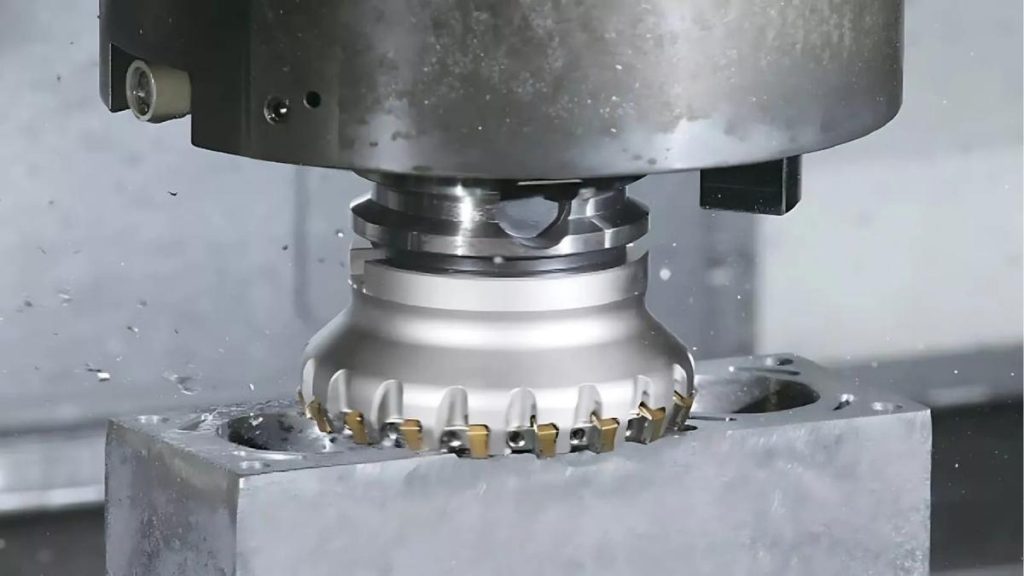

Milling a flat surface constitutes one of the fundamental operations in industry. The cutter machine operates along a path that matches the surface of the workpiece. A flat surface emerges via material removal from the workpiece surface through this operation. The procedure finds its main application in achieving consistent flat surfaces.
Plain milling depicts excellent effectiveness when performing surface preparations. The surface cleanup of parts needs this operation as your most effective solution. It represents a standard operational practice in numerous workshops to make flat and smooth surfaces on metal parts.
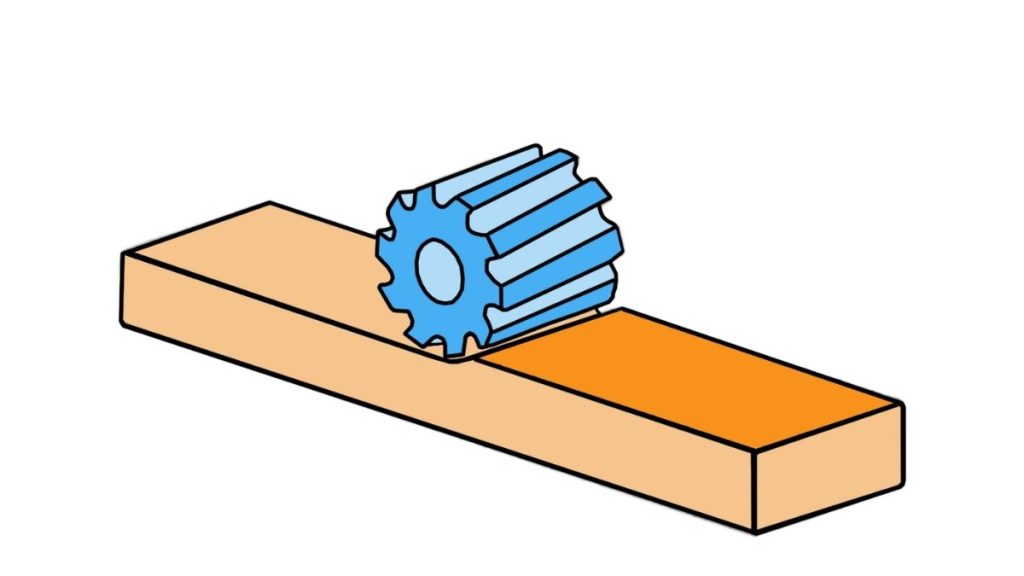
The key objective of side milling is to shape the edges of components. The cutting tool operates along the material edges to produce flat vertical surfaces. The milling operation primarily serves to create grooves and slots in workpieces. It’s also used when parts need fine edge detailing or narrow cuts.
These processes help create the desired contours of the workpiece. Side milling provides accurate outcomes for basic grooves and extensive channels within the manufacturing process.
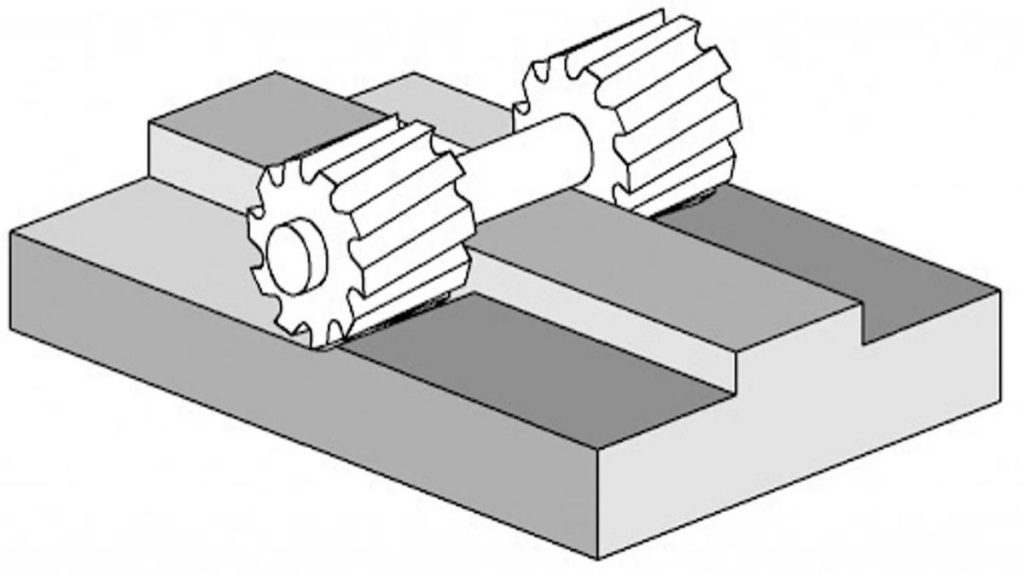
The combination of two cutters during straddle milling constitutes an exclusive machining procedure. It requires two cutters to machine parallel surfaces simultaneously on the workpiece. These cutters operate concurrently by being mounted onto the same arbor. Finishing two parallel surfaces within one continuous milling movement offers valuable benefits. It’s useful when parts need two equal sides cut at once.
Besides, it improves production efficiency and minimizes processing/cycle time. Straddle milling is considered an optimum choice for machining parts that possess several parallel sides. Predominantly, it is used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
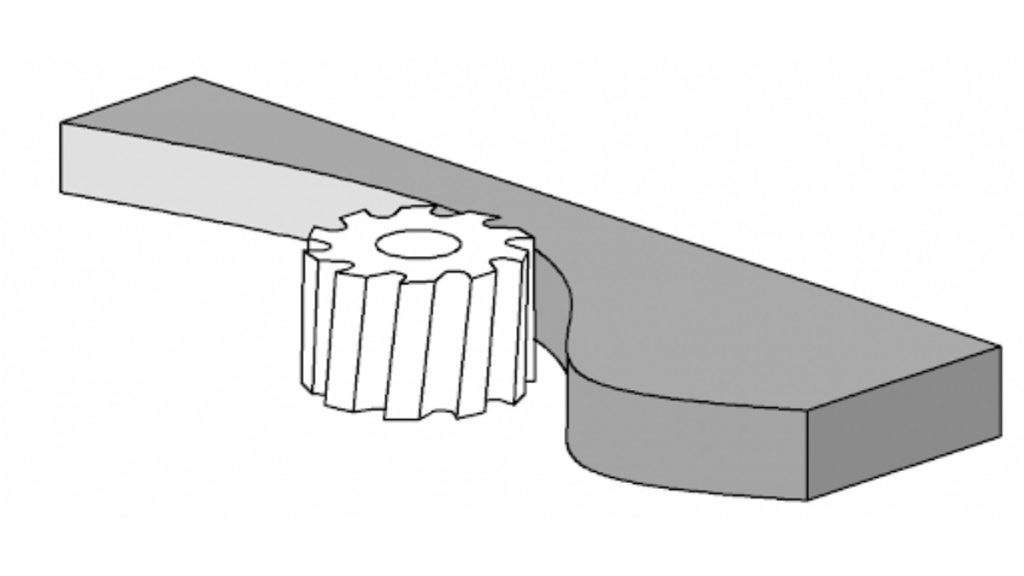
Gang milling operates with various cutters that simultaneously create multiple features. All cutters operate together on a single arbor. The Synchronized operation cuts multiple features from a part and increases the operation speed.
Multiple operations become obsolete when you conduct all necessary tasks at the same time through this process. This operation proves suitable for industrial mass production because of its high efficiency.

The process of angle milling requires material removal at a precise angular relation with the surface. It produces angled edges and slot features. Different mounting angles of the tool help users achieve target cuts.
It is vital for achieving accurate angular features during manufacturing work, such as when machining turbine blades in the aerospace industry or creating angled ports in automotive engine blocks. Moreover, working on intricate part designs requires this operation to fulfill your design requirements.

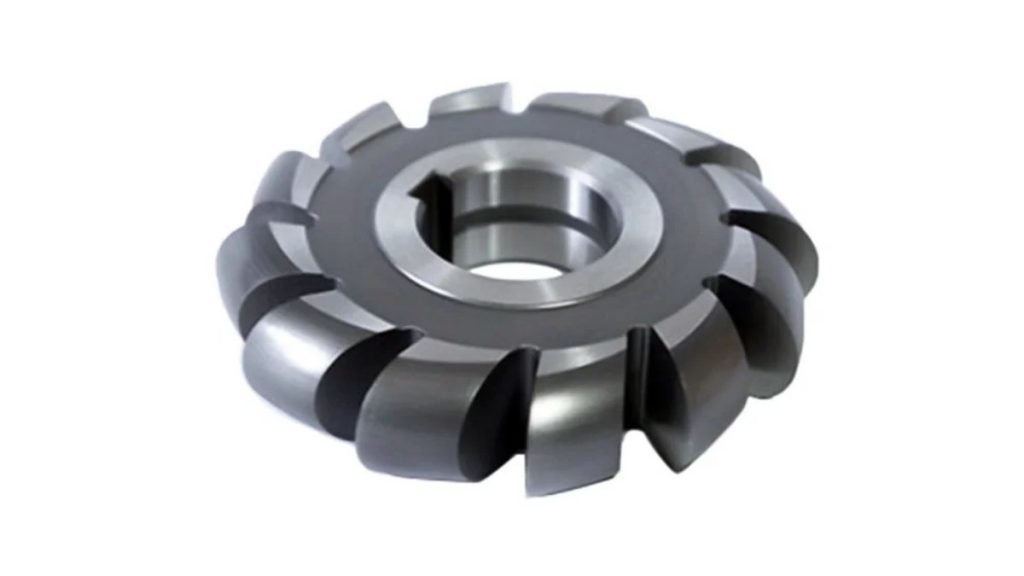
The process of form milling generates exact features by employing tools with particular forms. It involves cutting straight edges, shaping curves, and creating detailed patterns. The shape of the tool controls what geometric form appears in the cut.
It is perfectly suitable for producing specific, unique shapes. Form milling delivers high precision for gears and blades by accurately shaping complex profiles.

End milling stands as the most popular CNC machining operation in modern-day manufacturing. It has cutting edges that extend across its sides and its terminal points. It enables vertical and horizontal cutting motions, which provide multiple movement options for tools.
Machinists usually use this procedure to develop intricate shapes. In addition, it is effective for cutting intricate shapes within confined areas. Means it is used to cut detailed shapes and designs in small or hard-to-reach areas. Additionally, it can help produce unique shapes such as; pockets, grooves and contours in the material.
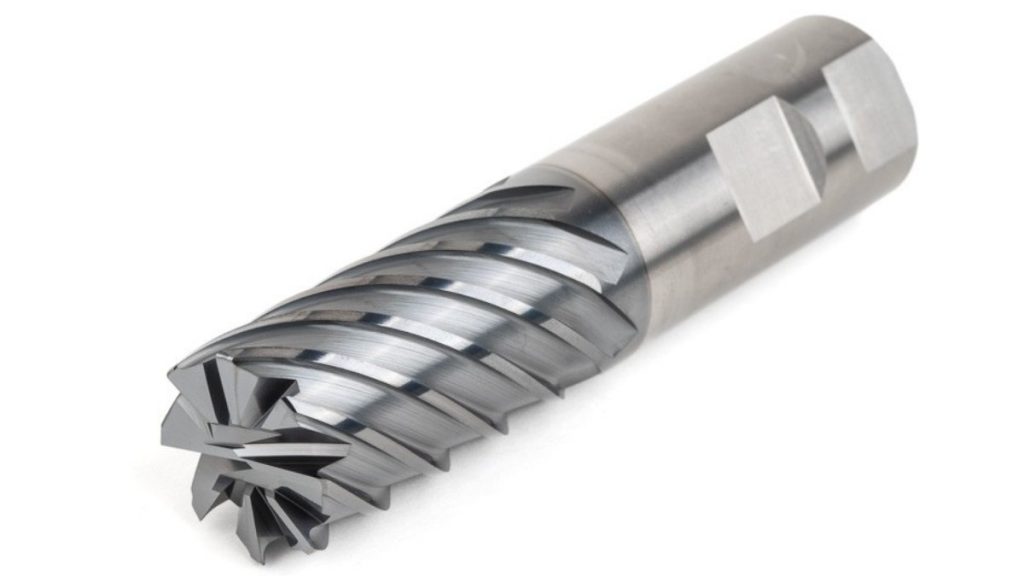

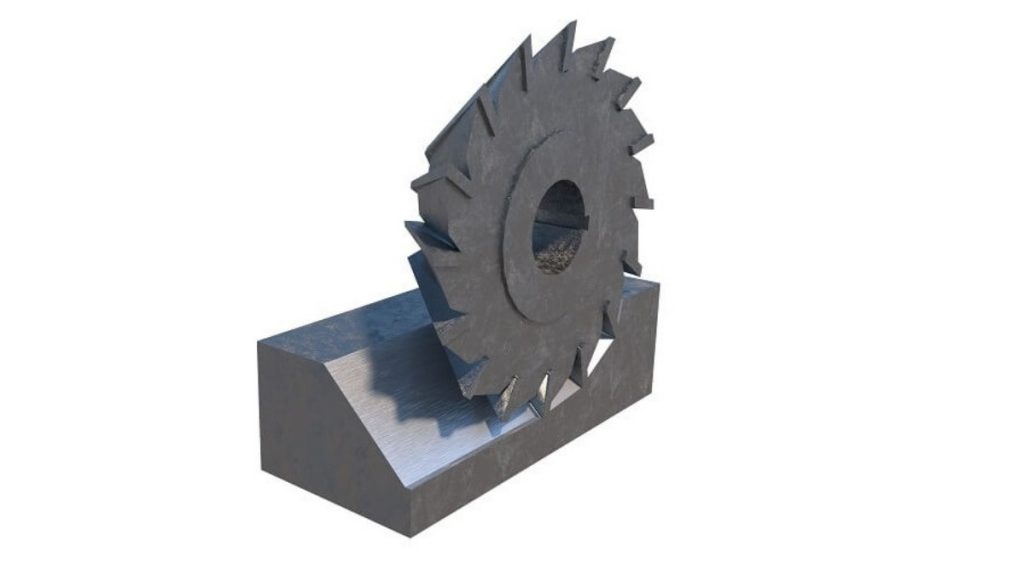
Saw milling allows the production of slots and the division of workpieces into separate sections. The saw-like cutting tool is used to cut deep perforations. The process finds its main applications in creating long slots and producing large material sections from original pieces.
A large material can be easily cut into smaller parts through this technique. The operation works as an effective method to cut through materials easily.
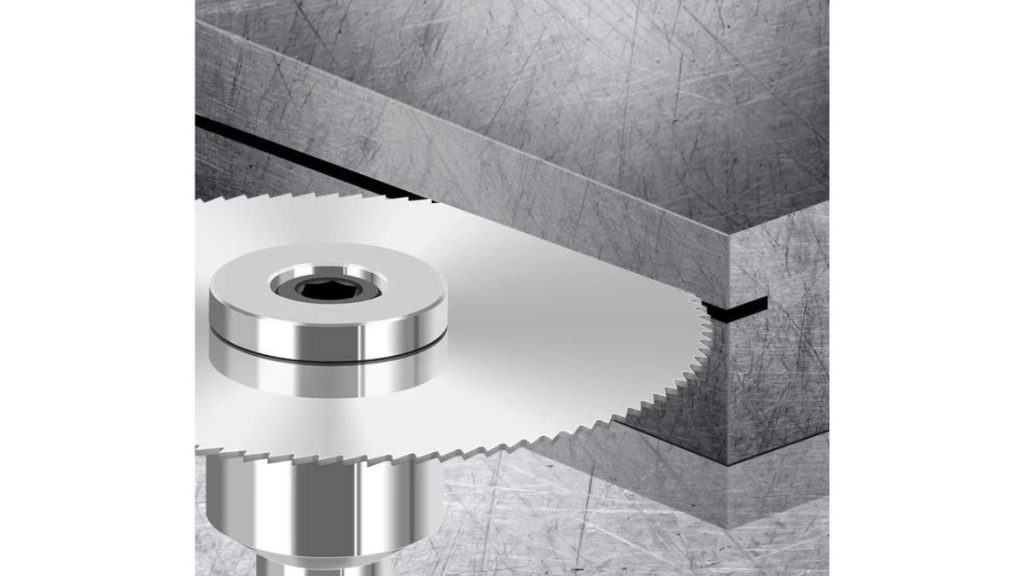
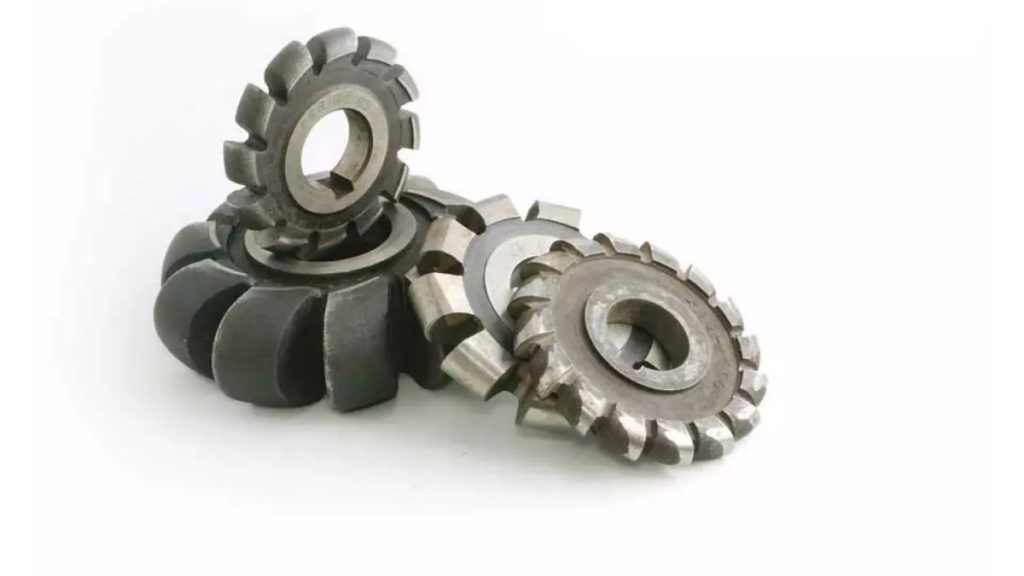
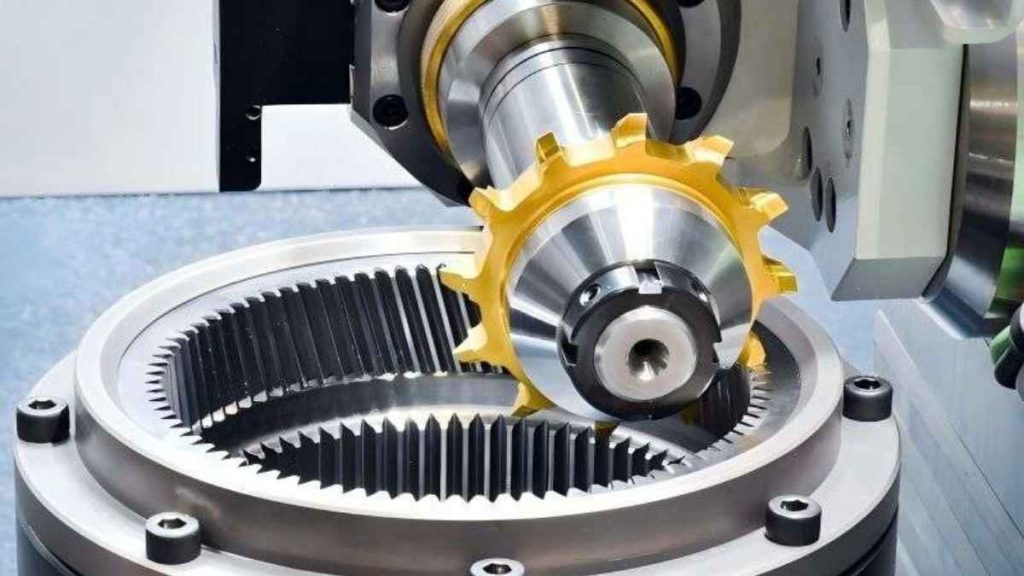
The specialized operation of gear milling serves for gear manufacturing purposes. The process employs a cutting instrument to develop teeth features on the job piece. A high level of control must be applied during the operation because it determines the adequate tooth angle and the space between teeth.
On the application side, gear milling plays a crucial role in industrial applications. Many manufacturing operations depend on gears and cannot function without them.. The precision and speed of tooth cutting depend on this operation when you are working with simple or complex gears.

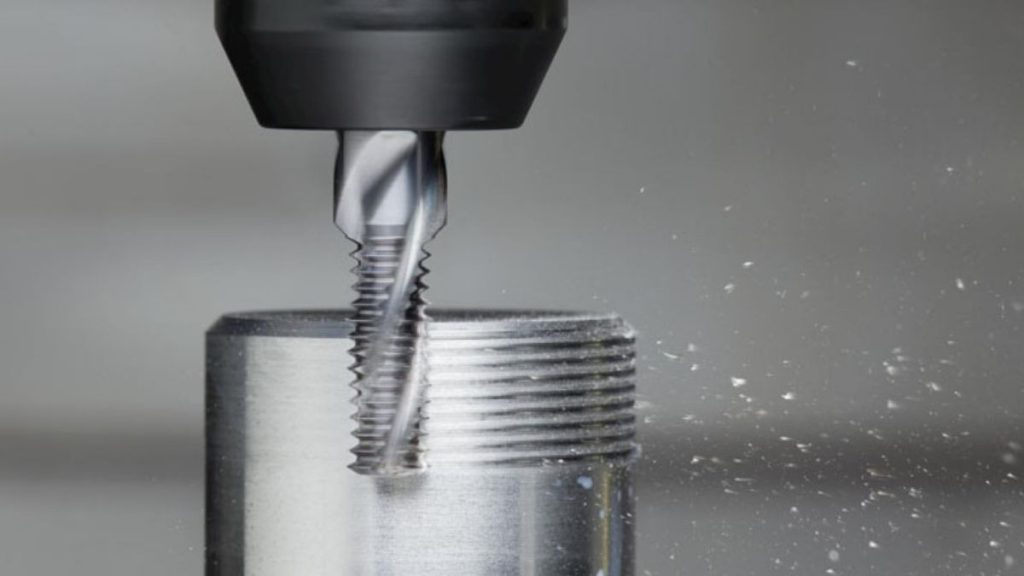
Thread milling helps develop outer and inner threads. It enables material thread cutting without requiring additional tapping operations. Although it proves best where standard tapping tools would not work and it also functions effectively for detailed threading operations. It is ideal for forming perfect threads in various parts and hard to machine materials.

CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) milling operates as a state-of-the-art production technique. The software program oversees the milling process. It manages and controls all machine operations with precision. CAM allows the production of complicated designs that conventional techniques cannot achieve.
The operation finds wide application in manufacturing operations that demand exact precision in their manufactured components. In addition, complex geometries and design multiplication tasks are best completed through CAM milling operations.
Let’s talk about the different types of milling operations based on their underlying mechanisms.
Manual operation of the machine takes place through manual control. It enables you to operate the cutting instrument by hand. Achieving quality outcomes with this method requires expert handling.
It works best to achieve complete operational control when producing single pieces or conducting low/minimal production of tiny parts. The precision level achieved through it reaches high standards when operators perform it correctly. Although it takes longer than automated milling operations.
The computer operates every component of CNC milling machines through automated controls. Complex part manufacturing becomes possible through this technique because it delivers extremely precise results. The machines enable the production of multiple parts without human involvement, making them suitable for high-quantity manufacturing needs.
CNC milling tools perform their tasks quickly while minimizing operational mistakes. This method is the top choice for mass production and precise design. Your parts will consistently maintain tight tolerances because of the high precision achieved through this process.
The production industry utilizes conventional milling, integrated with climb milling as a fundamental milling approach. A conventional milling process requires the cutter to advance in the direction opposite to the workpiece progression. As a result, severe heat and tool wear develop. During climb milling operations, the cutter experiences smooth movement in the same direction used by the workpiece. Therefore, the resulting surface stands smooth, and the tools undergo minimal wear.
The preference goes to climb milling because of its efficient performance and high precision level when compared with conventional milling techniques. Some materials, alongside specific setups, require conventional milling as an essential process.
Choosing the right milling operation depends on several factors. Here are the key elements to consider:
Successful material milling depends on selecting the appropriate techniques. The material nature determines the required milling speed because hard materials require slowness. While soft materials can tolerate faster speeds.
Milling operation depends heavily on the required finish quality. A smooth surface requires face milling as the most appropriate operation. When dealing with intricate forms, you should select either end milling or form milling operations.
The part consists of basic design elements with added complex features. Use a milling operation by considering the level of complexity that your part requires. End milling operations create precise cuts, yet plain milling serves best for flat surface production.
The equipment capabilities determine which machining technique you should choose. Some milling machines can only do certain jobs. Your machine's functional abilities determine the right operation selection.
The quality of work heavily depends on your choice of cutter. The various milling operations need specific cutter types. Use cutters that match your operations for the best performance outcomes.
Milling has become an indispensable technique in modern manufacturing. It has various approaches to create intricate patterns and geometries. Understanding of different types enables you to select appropriate manufacturing techniques. Your project can reach great success with a suitable milling approach that handles basic cuts to complex designs. However, choosing the right technique can be daunting, but don’t fret. The Apexrapid team is here to help you out. We help you choose the right milling option depending on material type and required finish quality, and the complexity of the parts. Reach out to our team for guidance or get an instant quote for your manufacturing project.
