Vacuum casting offers a practical solution for creating detailed parts quickly. You can use this process for prototypes or small production runs. It works well when you need quality parts without expensive tooling. The method uses silicone moulds and polyurethane resins to replicate your designs accurately.
At ApexRapid, we understand your project timelines matter. We've refined our vacuum casting services to support your goals effectively. Our team works carefully to deliver parts that meet your exact specifications. You'll receive components with excellent surface finishes and precise details.
No matter if you're making a new product or testing an idea, we're here to help. Our method is simple and works every time. During your project, you can expect clear communication and results that are always the same. We are proud to help engineers and designers with reliable manufacturing solutions that stay within your budget and meet your deadlines.
We'll go over the basics of vacuum casting in this article. You'll find out how the process works and why it works. We'll look at the different materials that are available and how they can be used in different fields.
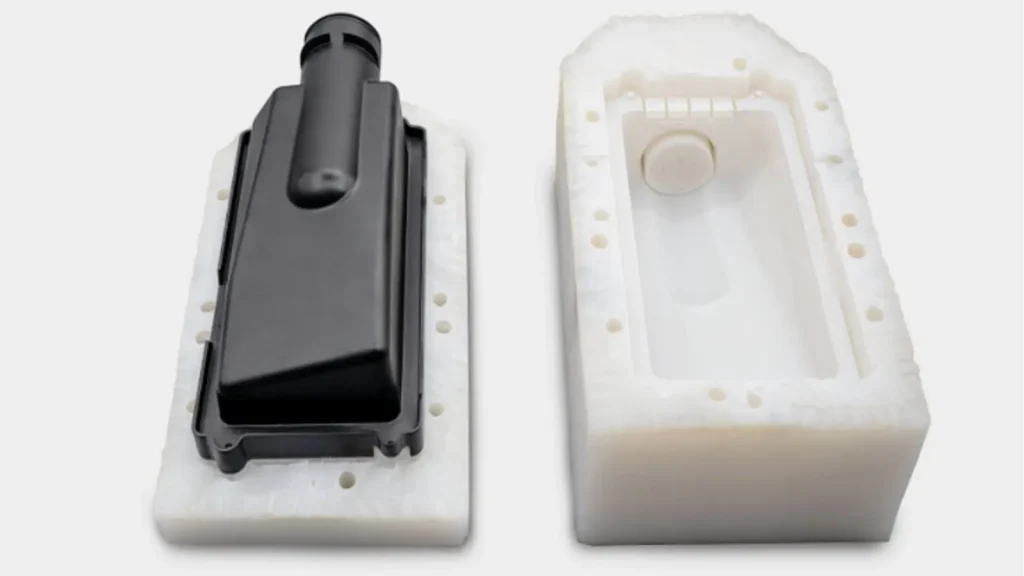

Vacuum Cast Finished Part
Vacuum casting makes high-quality plastic parts by using silicone molds and polyurethane resins. A master model, which is usually 3D printed, is the first step in the process. This master is surrounded by liquid silicone rubber that makes a mold. After it has dried, the mold opens and lets the master pattern go. Then, you pour polyurethane resin into the mold while it is under vacuum. The vacuum gets rid of all the air bubbles during the casting process. This makes sure that the surfaces are smooth and the details are copied exactly.
Every mold makes between 20 and 50 parts that are always the same. This method is great for prototyping and small production runs. You get the same quality as injection molding without having to spend a lot on tools. It's perfect when you need parts quickly for testing or small-scale production. This method works well for runs of 10 to 100 parts.
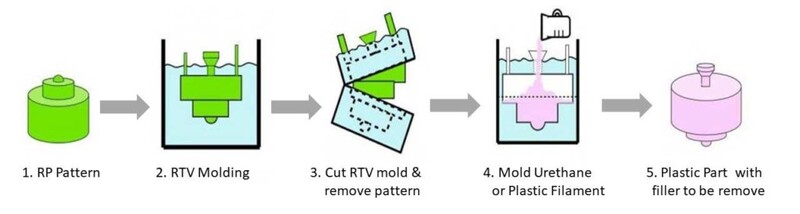
Vacuum Casting Process
Knowing how vacuum casting works can help you plan your project better. There are clear steps in the process from design to finished parts. We've explained each step so you know what to expect. This helps you get ready the right way and know when things will happen.
The first step in your project is to make a master model. For this step, we usually use 3D printing. The master needs to be exact and thorough. If there are any flaws on the master, they will show up on your parts. Before we move forward, we check everything very carefully.
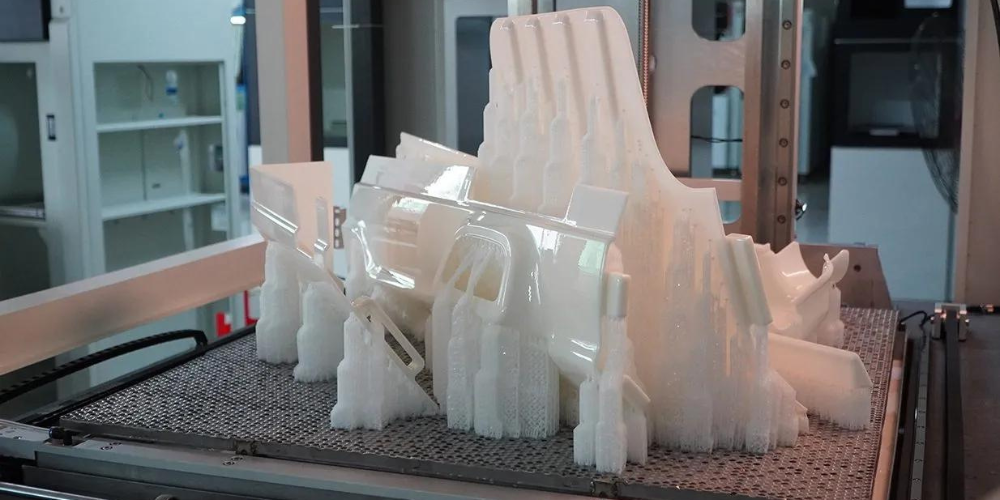

Master Model Creation
We put your master model inside a box that makes molds. Liquid silicone rubber flows in layers around it. It takes 16 to 24 hours for the silicone to harden. After that, we cut the mold and take out the master. This makes a hole that fits your design perfectly.
Before use, the mold is cleaned very well. We use release agents to make it easier to take parts off. The polyurethane resin is mixed in exact amounts. Before the casting can start, everything must be ready.
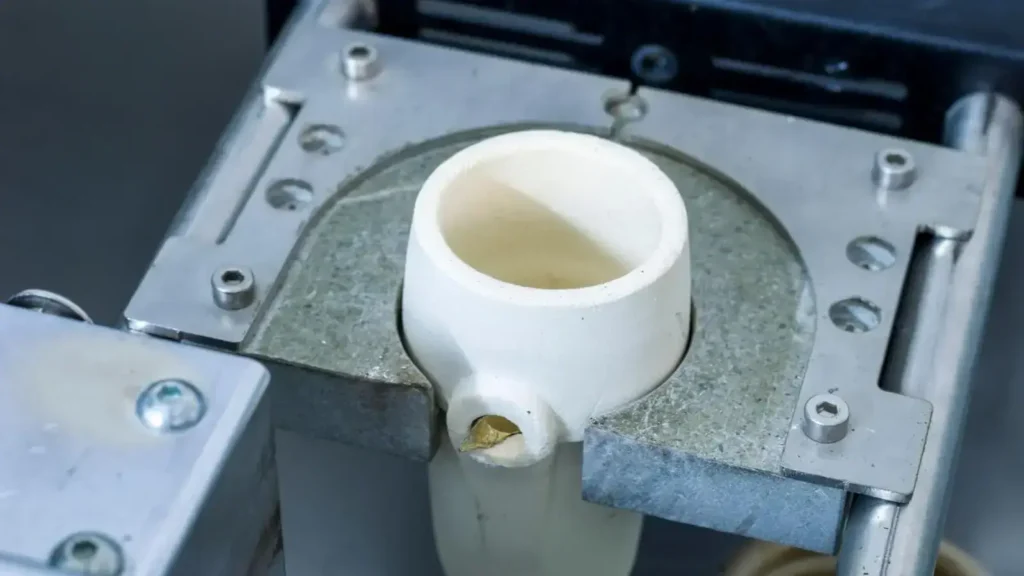

Casting process
The mold goes into our vacuum chamber. Resin flows through the gates into the hole. The vacuum pulls resin into every nook and cranny. This step gets rid of air bubbles. We keep an eye on the process to make sure it fills correctly.
The parts you make will cure inside the mold for hours. The type of resin affects how long it takes to cure. Some materials need to be heated up more. We wait until the parts are strong enough.
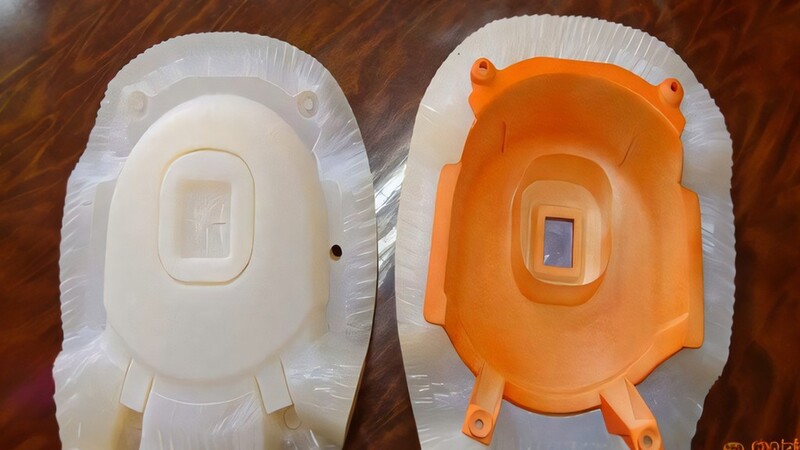

Plastic Vacuum Casting Part
We carefully take your parts out of the mold. Extra material is cut off cleanly. We check each part against your requirements. We carefully check the size and quality of the surface. Only parts that have been approved are put in boxes for delivery.
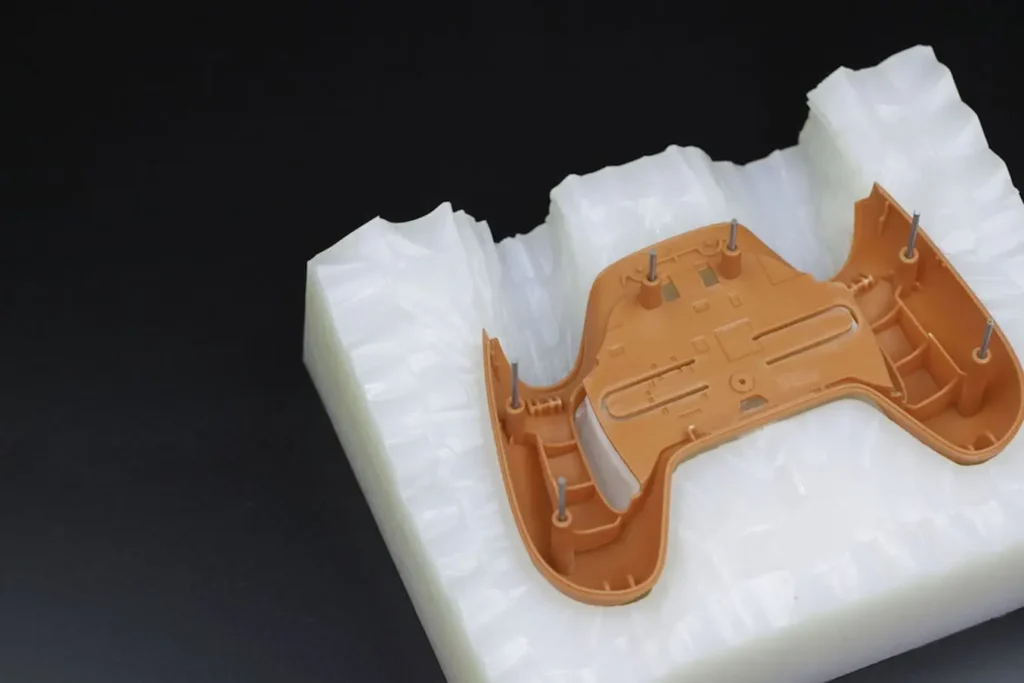

Urethane Casting
People often want to know if vacuum casting and urethane casting are the same techniques. The short answer is that they are pretty much the same way to make things. Both terms refer to the process of pouring polyurethane resin into silicone molds. The confusion comes from the fact that different companies use different names for the same services.
The word "urethane casting" is based on the material used. It shows that polyurethane resins are what make the final parts. "Vacuum casting" focuses on the environment in which the process takes place. It talks about how vacuum pressure takes air out of the mold when casting. Both names refer to the same way of making things.
Different areas and businesses have different words they like to use. A lot of the time, European manufacturers use the term "vacuum casting." Some American companies like to use "urethane casting" in their ads. In technical writing, you'll see both terms used to mean the same thing. The name doesn't matter; the process does.
The process stays the same no matter what name you use. First, master patterns are used to make silicone molds. Polyurethane resin is poured into a mold while there is no air. The vacuum gets rid of air bubbles, which makes the part better. It doesn't matter if you call it urethane or vacuum casting; the results are the same.
When talking to manufacturers about projects, make sure to be clear about what you want. Inquire about tolerances, lead times, and available material options. Make sure they have the right kinds of resin for your needs. You don't need to worry about what word they use for the service. Focus on whether they can meet the needs of your project well.
Vacuum casting uses different techniques depending on what you need. Each method helps with a different problem that might come up in manufacturing. We'll go over the main methods so you can see what your options are. This information is helpful when you talk to manufacturers about your project.
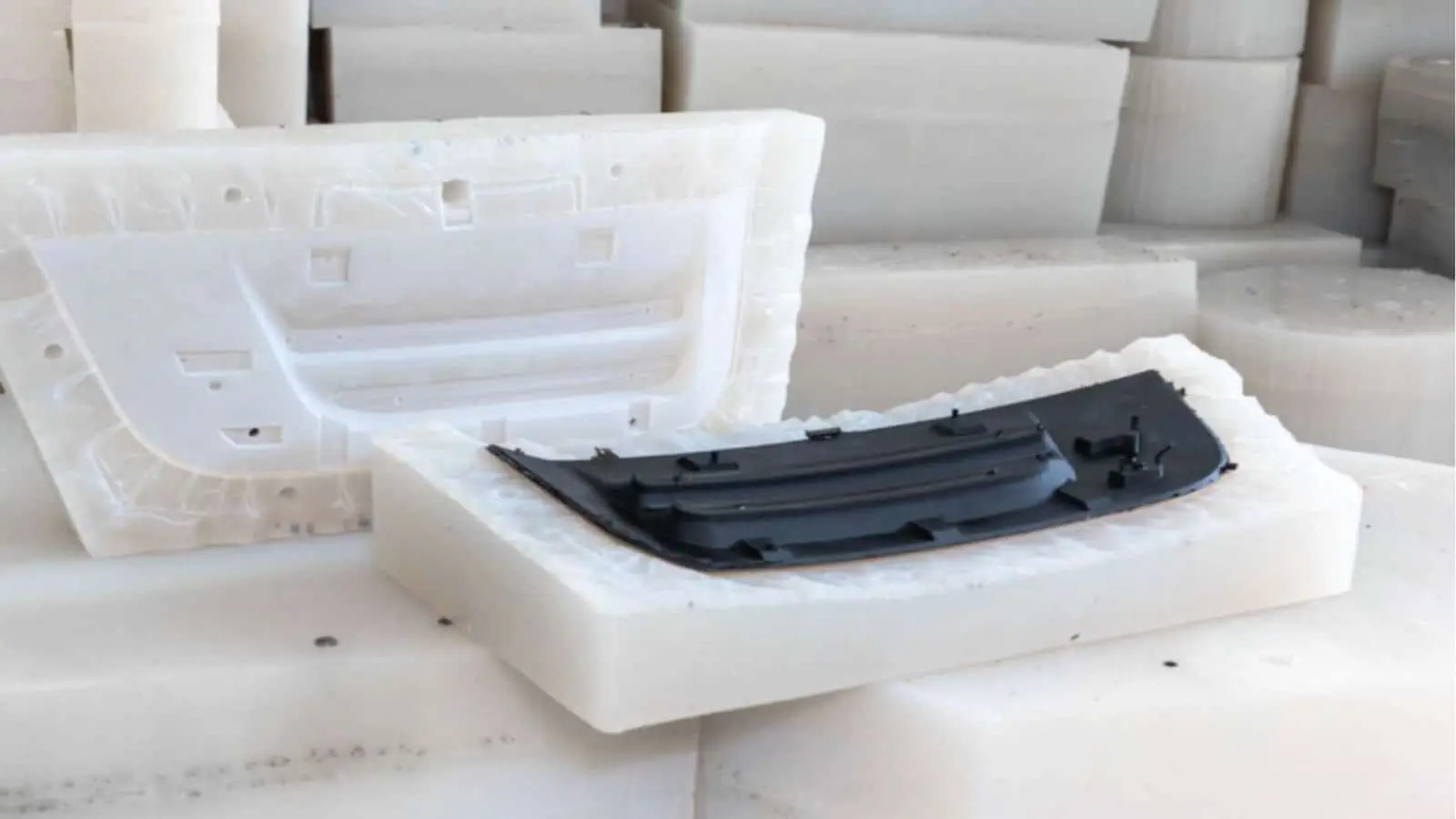

Vacuum Cast Mold
This method makes one piece at a time in the mold. It works well when you need to pay close attention to each part. This will be helpful for prototypes or designs that are hard to make. The method lets you check and make changes between castings. It's a good choice if you only need to make a few things.
Multi-cavity molds make a lot of the same part at once. This is a time-saver when you need more than one copy of the same part. All parts are cast at the same time and in the same way to make sure they are the same. When making matching sets or assemblies, you'll like this method. It cuts down on the total cost per part by a lot.
Overmoulding adds a second layer of material to a part that is already there. You might want a soft rubber grip on a tool made of hard plastic. During the casting process, the technique connects different materials. It gets rid of the need to glue or put together separate parts. You get a finished product that works and feels good.
This method starts by putting metal or plastic inserts inside the mold. During the process, the resin then casts around these inserts. This is how you can add threaded inserts, magnets, or metal pins. These parts are permanently inside the finished part. It's great when your design needs metal strength in certain places.
While the resin hardens inside, rotational casting spins the mold. This makes parts that are hollow and have walls that are the same thickness all the way around. You will use less material and still make the part strong. The method works great for bigger containers or enclosures. It's a cheap way to make light protective cases.
Some molds work better when pressure is added during the casting process. This makes it easier for resin to get into tight spaces and small details. This method gives you better surface quality on shapes that are hard to make. The best results come from using both vacuum and pressure. It's helpful when your design has walls that are very thin or features that are very complicated.
To make good parts consistently, vacuum casting needs special tools. Every machine is important to the process. Knowing how this equipment works makes you appreciate how much money manufacturers put into it. The quality of the equipment has a direct effect on the parts you get. We'll tell you about the most important machines used in the casting process.
Vacuum chambers make the controlled environment that casting needs. These sealed units work well to get rid of air in the mold cavity. Most chambers work at a pressure of 0.1 to 0.2 bar. The size changes based on what parts are being made. Bigger chambers can hold bigger molds and more than one piece at a time.
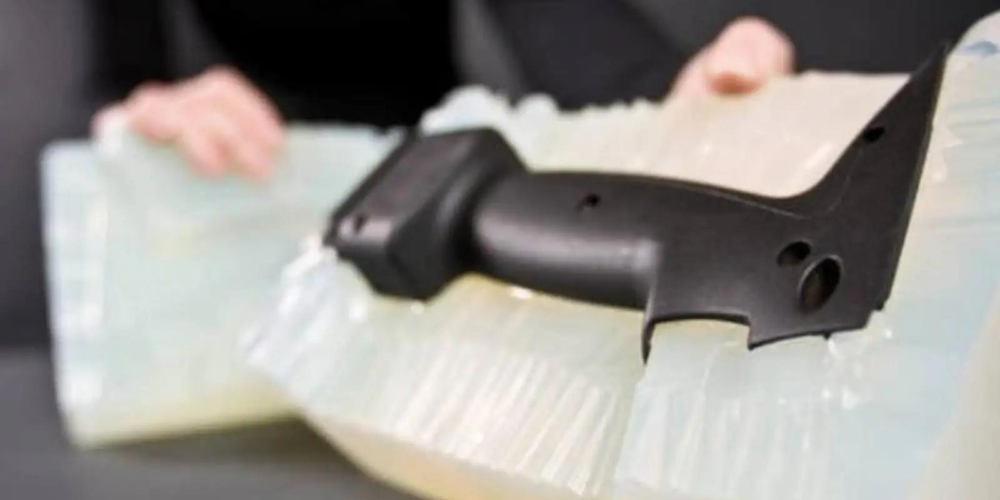

Filling the Mold Under Vacuum Conditions
Precise mixing equipment accurately combines parts of polyurethane resin. The machines measure and mix parts A and B. For the properties of the material and curing, it is very important to use the right mixing ratios. Automated mixers make sure that all of your cast parts are the same. Some systems have degassing features that get rid of air bubbles that are stuck.
Curing ovens give off heat in a controlled way to speed up the hardening of resin. To get the right strength in a material, you need to be able to control the temperature. Most ovens keep their temperatures between 60°C and 80°C very well. They make sure that the heating is even all the way through the curing cycle. Some resins harden at room temperature without the help of an oven.
These systems accurately pour liquid silicone rubber around master models. Controlled dispensing stops air from getting trapped while making molds. The equipment keeps the flow rates steady so that the mold thickness is even. Precision dispensing cuts down on material waste and makes the mold better. Some systems work in a vacuum to get rid of bubbles while pouring.
Specialized cutting tools carefully open silicone molds along the lines where they meet. Sharp blades make sure that cuts are clean and don't hurt the details of the mold. Trimming tools get rid of extra resin from cast parts very accurately. Different jobs can be done with both hand tools and powered tools. Good cutting tools make molds last a lot longer.
Digital callipers and micrometres make sure that the sizes of parts are right. CMM machines compare complex shapes to your original plans. Surface finish gauges check how smooth and textured a surface is. These tools make sure that every part meets your exact needs. Regular checks find problems early in the production process.
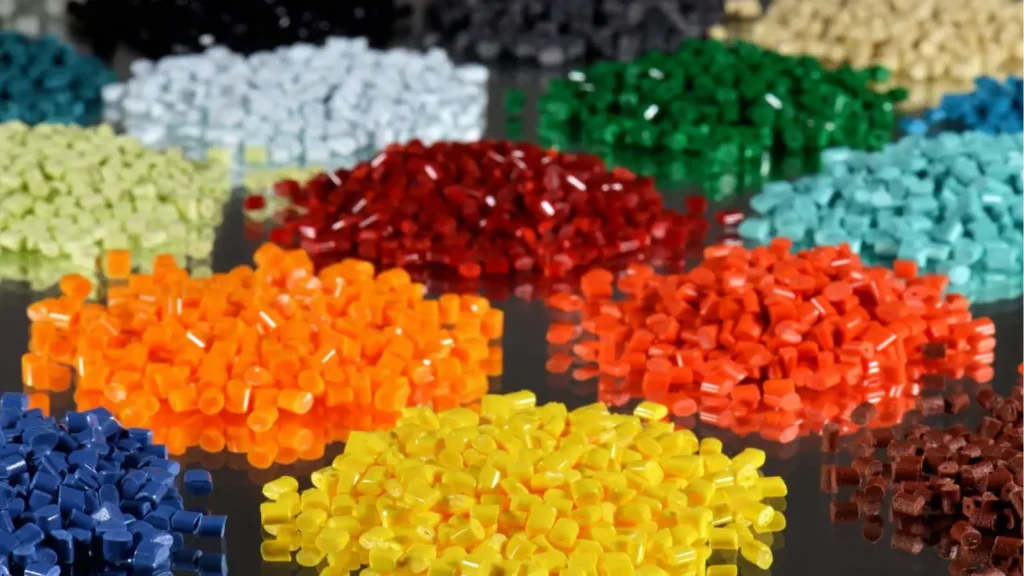

Material for Vacuum Casting
Choosing the right material for your vacuum-cast parts is important. Different polyurethane resins offer various properties to match your needs. We're happy to help you select the best option for your project. Each material type serves specific purposes and applications. Let's explore what's available so you can make an informed choice.
The most common materials used in vacuum casting are standard resins. They do a good job of copying the properties of common plastics like ABS. These are fine for most testing and prototyping needs. They are strong and won't break the bank. If you're not sure which material is best for you, we suggest starting here.
When you need them to, flexible resins make your parts feel like rubber. You can choose how hard you want it to be based on what you need. These are great for grips, seals, and other parts that need to be protected. The material bends and flexes without breaking or cracking. If you need samples to see the difference, please let us know.
For building things, rigid resins are very strong. Your parts will keep their shape even when they are under stress and weight. These materials work well for housings, brackets, and parts that hold weight. They work well for parts that need to work well for their intended purpose. We're happy to help you figure out if rigidity works for your design.
You can make beautiful, see-through parts with clear resins. They are great for display cases, light covers, or optical parts. The clarity can be anywhere from crystal clear to a little bit cloudy. We can help you get the level of openness you want. If you want, you can make things even clearer by using post-processing options.
Safety is important, and flame-retardant resins meet strict fire safety standards. These materials are very important for electronics and things that people can see. They slow down the spread of flames and greatly lower the risk of fire. We know about the different compliance requirements you might have. Please let us know what your safety requirements are so we can help you in the right way.
High-temperature resins keep their properties up to 150°C without fail. For use in cars or industrial equipment, you'll like these. Things won't get hot and make them bend or break. We're always here to talk about what temperature you need to run your business.
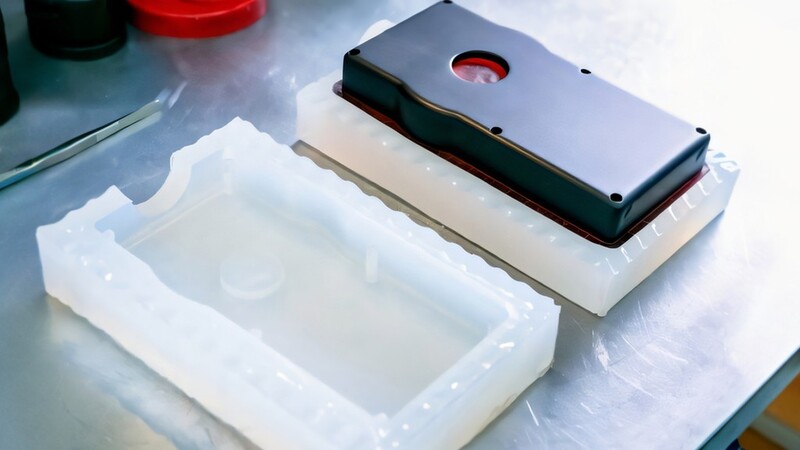

Applications of Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is used by many businesses that need high-quality parts fast. The method is good for both testing designs and making small batches of products. It will come in handy when the cost of traditional manufacturing is too high. Let's see where vacuum casting is most useful.

Vacuum Cast Parts
You can try out your designs in real life before spending a lot of money on tools. Vacuum casting makes functional prototypes that act like real products. This helps you find problems early, when they are easier to fix. It's cheap to make and compare different design versions.
Car makers use vacuum casting to make trim pieces and parts for the inside of cars. This is how most dashboard parts, knobs, and bezels are made. You get parts that fit and work like the ones that are made. This lets you try everything out in real cars first.
Medical equipment always needs materials that are safe and precise. Vacuum casting makes cases for surgical tools and diagnostic devices. The parts are accurate and clean enough for use in healthcare. You can make prototypes that can be used for clinical testing.
Electronics need protective cases that fit their internal parts perfectly. Vacuum casting makes enclosures, buttons, and connector covers that fit perfectly. You can see how people use your device. The finish looks and feels like it was made for the final product.
Vacuum casting helps with the development of everyday items. Things like kitchen tools, bathroom accessories, and decorative items work well. You can try out colors and finishes before making a lot of them. Small batches become cheap for products that are only available in small amounts or that are only available for a short time.
Many times, industrial machines need special parts or parts that are the same as the ones that broke. Control panels, protective covers, and fixtures can be made quickly with vacuum casting. The parts work well even in tough conditions. Faster part availability means less downtime for your equipment.
Surface finishes make your vacuum-cast parts look better and work better. Different finishing options work better for some products and uses than others. You can choose finishes that are exactly what you had in mind for your design. These treatments make things last longer and look a lot better. Let's look at the different ways you can finish your parts.
Parts come straight from the mold with little processing. The surface is a perfect copy of the mould's texture. You get a natural look that is smooth and matte. This choice keeps the cost of prototypes low. It works well when looks don't matter.
Sanding gets rid of small flaws and makes surfaces smoother. Polishing makes clear parts shine and makes them easier to see. You can get different levels of gloss, from matte to high gloss. This finish is good for parts that need to look professional. It's common for products that are aimed at consumers.
Painting adds color and does a good job of protecting the material underneath. You can match certain brands or color codes. Multiple coats make parts last longer and cover them evenly. Primer layers make paint stick better and last longer. This finish makes parts look like they are ready for production.
Powder coating makes a strong, smooth finish that lasts. The coating is better than paint at resisting scratches, chemicals, and wear. You get the same color on all the parts in a batch. It's great for handling parts, using it a lot, or in tough conditions. The finish looks good and lasts a long time.
Vacuum casting creates quality parts quickly using silicone moulds and polyurethane resins. The process suits prototyping and small production runs of 10 to 500 parts. You get low tooling costs and fast lead times compared to traditional manufacturing. Tolerances reach ±0.05 mm for precise components. Multiple material options match different application needs. Industries use this method for complex geometries before mass production. Each mould produces 20 to 50 parts reliably.
ApexRapid delivers precision vacuum casting with lead times as fast as 2 days. We offer tolerances up to ±0.1 mm and multiple material options. Our team guides you through the entire process professionally.
Get Instant Quote | Contact Us Today
Here are answers to common questions about vacuum casting. We've kept responses brief and straightforward to help you quickly.
Vacuum casting creates parts by pouring polyurethane resin into silicone moulds under vacuum. The vacuum removes air bubbles for smooth, accurate parts. You start with a master model, create a silicone mould, then cast multiple copies.
For parts under 100 mm, you can expect ±0.1 mm precision. Larger components typically achieve ±0.3% of the dimension. These tolerances suit most prototyping and small production needs.
Silicone moulds typically cost £200 to £800 per mould. Individual parts range from £10 to £80 depending on size, material, and finishing. It's more affordable than injection moulding for small quantities.
Always wear nitrile gloves and chemical splash goggles when handling resins. Use organic-vapour respirators in well-ventilated spaces. Handle heated moulds with thermal gloves. Be careful with vacuum chamber closures.
Add at least 1° draft angles to vertical walls. Use fillets on internal corners instead of sharp edges. Keep wall thickness between 1.5 mm and 4 mm. Plan mould split lines carefully for easy part removal.
We verify resin mix ratios by weight before casting. Dimensional accuracy is checked using CMM or laser scanning. Visual inspections catch surface defects early. Batch testing ensures consistent mechanical properties.
Material waste is typically less than 5% per project. Silicone moulds are reusable for 20 to 25 cycles. Some resins contain VOCs, but bio-based alternatives are increasingly available.
Vacuum casting has lower tooling costs (£200-£800 vs £10,000+) and faster lead times (10-20 days vs 4-12 weeks). It suits volumes of 10 to 500 parts. Injection moulding becomes more economical above 500 units.
Vacuum casting provides better surface finish and consistency for batches. 3D printing offers more design freedom for one-offs. Vacuum casting works better for 10+ identical parts. 3D printing suits rapid single prototypes.
Look for experience with your industry and part type. Check their equipment quality and material options available. Verify ISO certifications for quality assurance. Ask about lead times and communication processes. Request sample parts if possible
