In automotive design, no two parts are ever the same. Each model brings new design demands, new materials, and tighter tolerances. Engineers often struggle to turn digital designs into physical components that actually perform. Issues like tool wear, uneven surface finish, and small fit errors can cause delays or rework. On top of that, deadlines are short, and testing cycles leave no room for guesswork. That’s where practical manufacturing support makes the difference.
At ApexRapid, we work with engineers every day to solve these challenges. When you send us a design, our technicians review it for manufacturability before cutting the first piece of metal. We look for thin walls, deep pockets, and tolerances that could affect production. With CNC machining, injection molding, and sheet metal fabrication all under one roof, we can adjust processes quickly if something needs fine-tuning. This approach saves time and helps keep projects on schedule without sacrificing quality.
Our job is to make sure your parts fit, function, and hold up in real conditions. We use strong and reliable materials like aluminum, steel, and engineering plastics for different automotive applications, from brackets and housings to small precision fittings. Every part is inspected before shipping, so you know it will meet your design specs.

Custom Automotive Parts
Custom automotive parts are made to fit a specific vehicle or project. They are not standard or off-the-shelf. You use them when regular parts cannot meet your design, strength, or performance needs.
These parts can be small brackets, mounts, engine components, or body panels. Each part is made to precise measurements so it works correctly in real conditions. Materials and shapes are chosen to handle stress, heat, and vibration.
Engineers rely on custom parts for testing, prototypes, and performance upgrades. They help you solve fitment problems, improve efficiency, or validate new designs. Without them, projects may face delays or fail to meet goals.

Robotic Automotive Manufacturing
Custom automotive parts or components are produced through various processes to address a certain demand. Depending on the material, shape, and quantity of parts required by the engineer, the appropriate technique is selected. Both of these techniques contribute to the production of parts with good fit, good working efficiency, and good production speed.
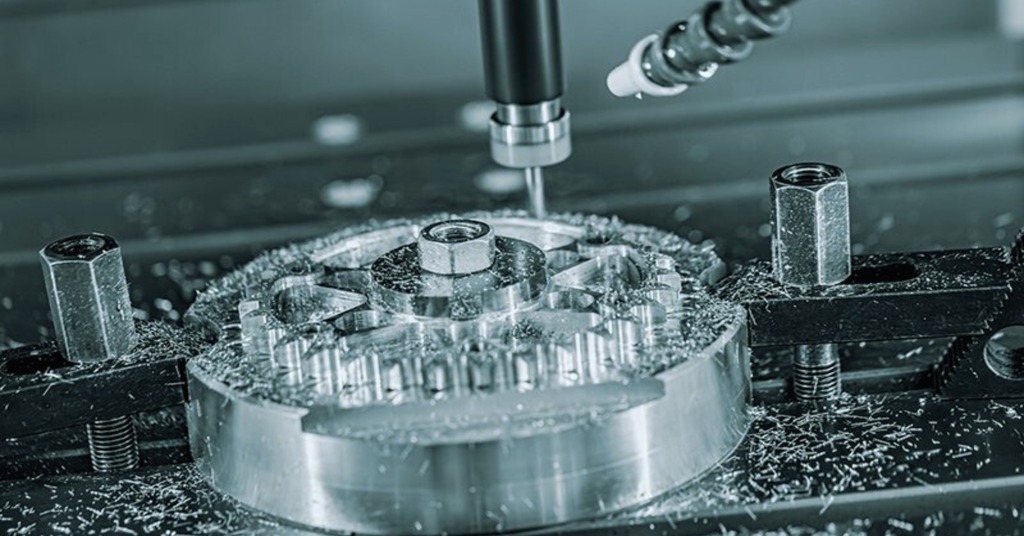

CNC Machined Automotive Part
CNC machining involves metal or plastic with computer-controlled cutting tools. It is applied for making engine parts, brackets, mounts, and parts that require precision and exact dimensions. It guarantees the perfect fit of parts and their operation under stress.
Moreover, it is used to produce a quick change in designs. You can customize sizes or features and generate new parts in a short period of time. It is effective with the small lot, prototypes, and even high-volume production lots. Multi-axis CNC machines allow to creation of a curved path or angle without additional arrangements.
Injection molding produces products by pressing the melted plastic into molds. It has wide application in clips, panels, components of housings, and other interior components. Molds are made by engineers in such a way that they do not warp, have no voids, or are not of uneven thickness.
Using this technique, numerous automotive parts are manufactured in a short time. Engineers have the option of using alternative plastics or additives to enhance strength, heat resistance, and flexibility. It is best suited to medium-scale production where consistency and durability are of the essence.

Auto Assembly Workshop
Sheet metal fabrication entails cutting, bending, and shaping metal sheets into useful components. It is used by engineers in brackets, chassis supports, panels, and structural components. Bend allowance and thickness of materials should be meticulously calculated to avoid cracks and deformation.
High-precision holes and shapes are created through laser cutting and CNC punching. Bending and forming machines permit complicated angles. Welding, rivets, or adhesives can then be used to join the parts into strong and functional assemblies.
3D printing is used for making parts in layers using either plastic, resin, or metal. It is used in prototypes, low-volume, or parts whose internal structure is too complex. It permits designs that would have been impossible or prohibitively expensive to machine.
Fit, ergonomics, or even weight can be tested before full production. Iterations and revisions of the design can be done quickly by engineers without the use of expensive molds or tooling. Small production runs are also manufactured by some metal 3D printing techniques to produce functional parts.
Vacuum casting is used for the production of low-volume parts made using liquid resin that is poured into silicone molds. It is best suited to handle, trim, housings, and other fine objects. In general, first, the parts are checked for the appearance, fit, and feel of a component before commencing mass production.
Strong and smooth parts are provided with the vacuum as it blows away air bubbles. The material properties, color, and toughness can be modified and brought close to the actual production elements. It is a low-cost method of testing designs.
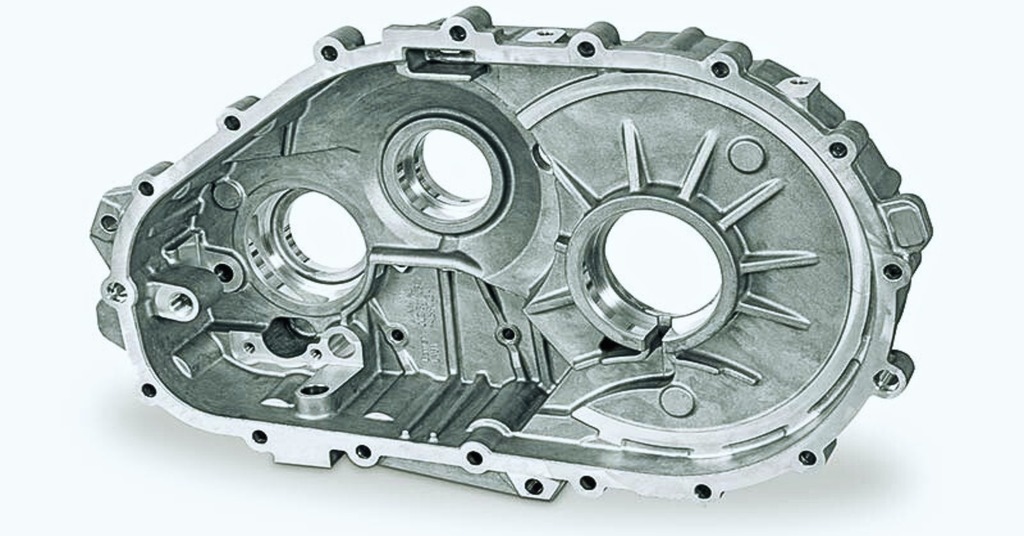

Die-cast Automotive Engine Part
Die casting entails high pressure of molten metal into a steel mold. It is used in brackets, engine components, and small metal components that are required to be strong and accurate. Design of the mold takes into account cooling, shrinkage, and ejection to avoid warping.
The process yields long-lasting, precise components that have smooth faces. Once cast, the engineers can machine critical features like threads or holes. Die casting is suitable for medium-to-large volume production where consistency and strength are the main considerations.
The wire EDM employs metal cutting through thin metal wire and electrical sparks. It is applied to the small, fine objects that have tight tolerances and complex internal forms. It can traditionally process hard-to-machine metals.
There is no stress or distortion in its process of producing clean cuts. Engineers use EDM in dies, molds, and other small engine automotive parts that need an ideal edge and intricate internal characteristics.
In extrusion, aluminum is forced through a patterned die to create long components of equal cross-section with uniform cross-section. It is used in rails, frames, supports, and structural components by engineers. The shape may be optimized in terms of strength, weight, and rigidity.
Parts which have been extruded may be cut, drilled, machined, or even joined. The choice of type and thickness of aluminum depends on the mechanical and environmental needs of engineers. Extrusion offers lightweight structural automotive components.
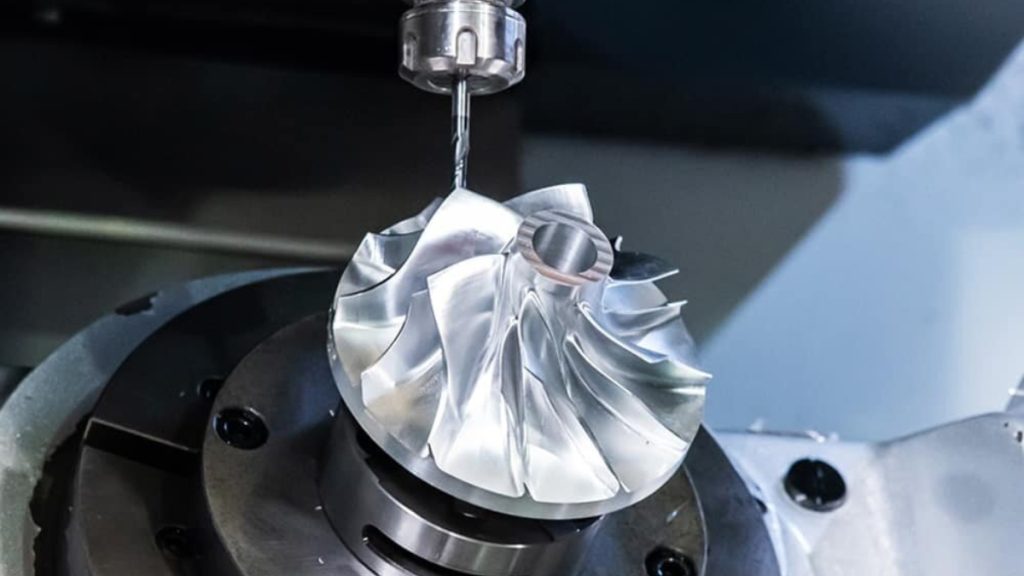

Custom Automobile Headlight Housing
The 5-axis machining involves the simultaneous tool movement in five directions. It is applicable in complex components that feature curves, angled parts, or deep cavities, which engineers use. It cuts down on installations and enhances accuracy.
It generates smooth surfaces and complicated geometries effectively. Suspension arms, engine brackets, or structural components with close tolerances can be engineered by engineers. The approach is useful when there is a prototype, a small volume of production, or when the part is of a complicated design.
Metals are essential for parts that demand strength, durability, and heat resistance. Here are the common methods used in custom automotive parts.
Aluminum is light, corrosion-free, and easily shaped. It is commonly applied in engine blocks, suspension arms, body panels, and heat sinks by engineers. It is lightweight and therefore has fuel efficiency, and heat-treated aluminum alloys are sufficient in terms of strength in high-stress regions.
Steel is tough, multi-purpose, and dependable. It is usually applied in chassis frames, brackets, safety beams, and load-bearing elements. The steels that are high in strength are used where the loads are heavy, vibrations, and repeated stress. Exhausts, fasteners, and parts that are in contact with moisture or chemicals are being used with stainless steel.
Titanium is hard but weighs less than steel. It is applied in high-performance engines, exhaust, and suspension components. Titanium can withstand elevated temperatures and overload, and thus can be fitted in racing or high-end cars. It is expensive and more difficult to machine. Therefore, engineers selectively use titanium for critical parts.
Though Copper and Brass are utilized as electrical and thermal components. Copper is the best choice for wiring, connectors, and radiators due to its high conductivity. Fittings, bushings, and small precision parts are made out of brass as it is durable and resistant to corrosion.
Magnesium is highly light and is commonly applied in gearboxes, engine covers, and steering parts. It decreases the vehicle's weight and enhances its performance, but it must be handled carefully during machining because it is flammable. It is made stronger or workable by alloying it with aluminum or zinc.

Transparent Auto-Car Plastic Product
Plastics are lightweight and permit intricate shapes. These are also versatile enough to be employed in other car models.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is solid and resistant to impact, and is usually applied to dashboards and interior panels as well as housings. Its dimensional stability promotes perfect fits in assemblies.
Polypropylene (PP) is elastic, resistant to chemicals, and is utilized in bumpers, fluid containers, and wraps. It is resistant to oils, fuel, and harsh chemicals.
Polycarbonate (PC) is hard, non-opaque, and heat-resistant. It is utilized by the engineers in headlights, instrument covers, and protective shields. PC may be used together with ABS to enhance impact resistance and finish.
Nylon (PA) is hard, low-friction, and resistant to heat. It is best suited to gears, bearings, cable guides, and moving parts. Glass fiber reinforced ones enhance stiffness and wear resistance.
Polyurethane (PU) is soft, strong, and shock-absorbing. It is applied in the suspension parts, gaskets, mounts, and bushings to absorb shocks and noise.
Plastics are also selected by engineers depending on strength factors, temperature resistance, exposure to chemical reaction of the material, and flexibility/rigidity of the part. Reinforcement with fiberglass or carbon fiber makes the structure more stable but not heavier.
Parts that are exposed to extreme temperature and friction or wear are best used in ceramics.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide) is hard, thermally resistant, and electrically insulating. It is applied in spark plug insulators, sensors, and brake parts. It has great wear resistance and thus a very long life when used in strenuous applications.
Silicon Carbide is highly resistant to thermal shock, and it is very tough. It is applied by engineers in high-performance brakes, turbocharger parts, and exhaust parts. It can withstand high temperatures and friction as compared to metals.
Zirconia is tough, wear-resistant, and thermostable. It is applied in bearings, valves, and in special engine parts where metals fail on their own.
Ceramics are brittle but effective when they are used with metals or polymers. They are commonly employed by engineers in hybrid components to obtain heat resistance and impact strength.
Designing and producing custom automotive parts is not easy. Engineers face several challenges that can affect quality, cost, and performance. Understanding these challenges helps you plan better and choose the right manufacturing solutions.

Auto Parts Manufacturing Materials
It is usually difficult to select the appropriate material. All metals, plastics, and ceramics respond differently to pressure, heat, or wear. Failure, shortened life, or performance can result from choosing the wrong material. The engineers will have to strike a compromise between the strength, weight as well and the cost, keeping in mind that the material should be easily processed.
Vehicle components may require very high tolerances. Working with even minor errors, one may face misalignment, vibrations, or safety issues. It involves elaborate machinery, operators, and quality control in each step to produce high-precision outputs.
Contemporary automobile parts demand complex shapes and features. Complex design is a challenge to produce and can involve several processes. Engineers are required to make sure that the component can be manufactured consistently without affecting the strength or functionality.
Custom parts are relatively costly to produce in small batches. Engineers have to discover how to design optimally, save on the amount of material used, and select effective production processes. It is usually a big challenge to balance cost and quality.
All components should comply with the performance and safety standards. Engineers perform tests of durability, heat resistance, vibration, and wear. Pieces might fail under the actual situation, and the recalls or damage take place without the necessary testing.
Precision Automobile Gear Component
Choosing the right manufacturer is critical for producing high-quality automotive parts. You need a partner who understands materials, precision, and performance. Here’s how to find one.
Select a manufacturer with proven experience in the automotive industry. They understand strict tolerances, safety standards, and material requirements. Experienced companies can spot potential design or production issues early, saving time and avoiding costly mistakes.
Different parts require different techniques. Ensure the company can handle CNC machining, injection molding, 3D printing, die casting, sheet metal work, or 5-axis machining if needed. Advanced equipment allows precise tolerances, smooth finishes, and faster production. Also, ask if they offer post-processing like heat treatment or surface finishing.
Automotive parts must be reliable and safe. Look for manufacturers that follow ISO 9001, IATF 16949, or similar standards. Ask about inspections, testing, and traceability processes. Companies with strict quality checks reduce defects and ensure every part meets specifications.
Custom parts use metals, plastics, and ceramics. A reliable manufacturer understands the behavior of each material under stress, heat, or wear. They can recommend alloys, plastic grades, or composites that improve strength, durability, and longevity. Proper material knowledge ensures parts function correctly in real-world conditions.
Check how quickly they can produce prototypes and small batches. Fast lead times help you test and iterate on designs. Flexibility is also important—your manufacturer should handle design changes, volume adjustments, or special requests without delaying the project.
Ask for case studies or references. Seeing examples of similar work shows the company’s technical ability, reliability, and consistency. It also gives confidence that they can meet your specific requirements.
Good communication is essential. A manufacturer should guide you on design improvements, material choices, and production methods. Prompt updates, technical advice, and problem-solving support make the production process smoother and prevent mistakes.
At Apexrapid, you will get parts that fit perfectly and perform reliably. Our CNC makes custom automotive parts using precise machining, 3D printing, injection molding, and die casting. We handle everything from material selection to final inspection to ensure your parts meet your needs.
Whether you need prototypes or full production, ApexRapid CNC delivers high-quality parts on time. Start your project today and get a fast, personalized quote.
