Aluminum heat sinks are an important part of many machines and electronic devices. They help control heat so the parts keep working smoothly. In most factories, these heat sinks are made through simple methods like extrusion or machining, depending on how detailed or strong the part needs to be. The goal is always to make the surface clean and the fins neat so the heat can move out easily.
Aluminum is a material of choice among engineers because it is light and strong. It is also easy to shape and carries heat better than many other metals. The right material grade and design make a big difference in how well the heat sink performs. A well-made one keeps systems running safely without overheating.
To make the part last longer, manufacturers sometimes add surface finishes like anodizing or basic coating. These finishing touches help protect the metal and give it a clean look. In the end, aluminum heat sinks quietly do their job, helping tools and machines stay cool and reliable every day.

Aluminum Heat Sink
Aluminum heat sinks are used to control heat in machines and electronic parts. When a device runs for long hours, it produces heat that can damage internal parts. A heat sink helps move that heat away. It keeps performance steady and parts safe. You’ll often see them in LED lights, computers, and power systems where steady temperature is important.
In production, aluminum is preferred because it’s light, easy to shape, and spreads heat fast. Manufacturers design the sinks with narrow fins or flat plates so air can flow easily and cool the surface. The shape, size, and finish all depend on how much heat the part needs to handle and where it will be used.
Aluminum heat sinks are designed carefully and meticulously. The procedure is efficient, durable, and performance-oriented. All the steps are intended to maintain the control of heat as per various applications.
It starts with the selection of an appropriate aluminum grade of 6061 and 6063 due to their combination of strength and easy machining. This is done to maintain the quality of all parts by checking every batch before use.
Depending on the design, manufacturers apply extrusion or casting. During extrusion, molten aluminum is forced through a die, creating fins. The casting of parts is employed when the parts require heavy bases or complicated shapes. The two techniques render the construction robust and prepared to cut.
Each piece is then cooled, followed by CNC machining. The spacing of the fins is adjusted, and mounting spaces are cut clean. The step makes the heat sink fit well in the actual machines and devices.
Circular Shape Aluminum Heat Sink
The parts are machined and then subjected to increased life. Avoiding corrosion and evenly heating by means of anodizing is common. Powder coating can also be required to enhance the protection of some projects.
All the heat sinks are checked and measured before shipping. Surface flatness, spacing, and rate of heat flow are checked by teams. In case changes are required by the client, the design is modified to suit and purpose.
Making aluminum heat sinks employs a process that is inclusive of thermal performance, cost, and production efficiency. Both methods have a direct impact on the ability of the heat sink to conduct heat and be integrated into electronics or equipment.
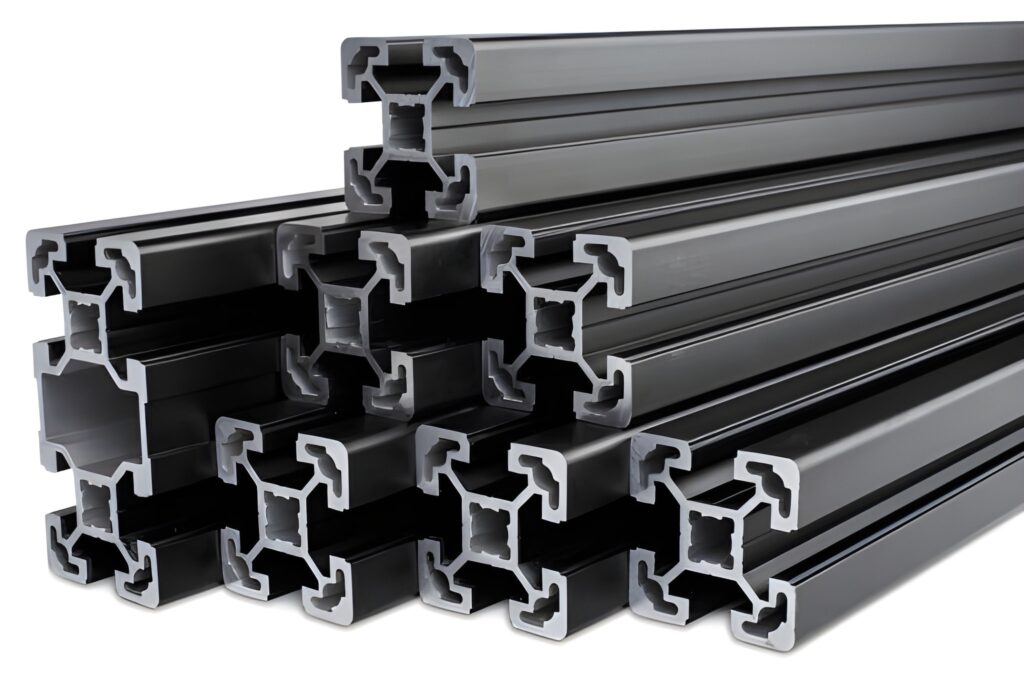

Aluminum Extrusion
In extrusion, a billet of aluminum is warmed up to a soft and, not melted state. It is then forced up into a die in the shape of the required pattern of the fin. The result of this is long profiles with straight fins, which are cut to length. Following extrusion, it can be machined to include mounting holes or might be machined to alter the thickness of the base to enhance contact with components.
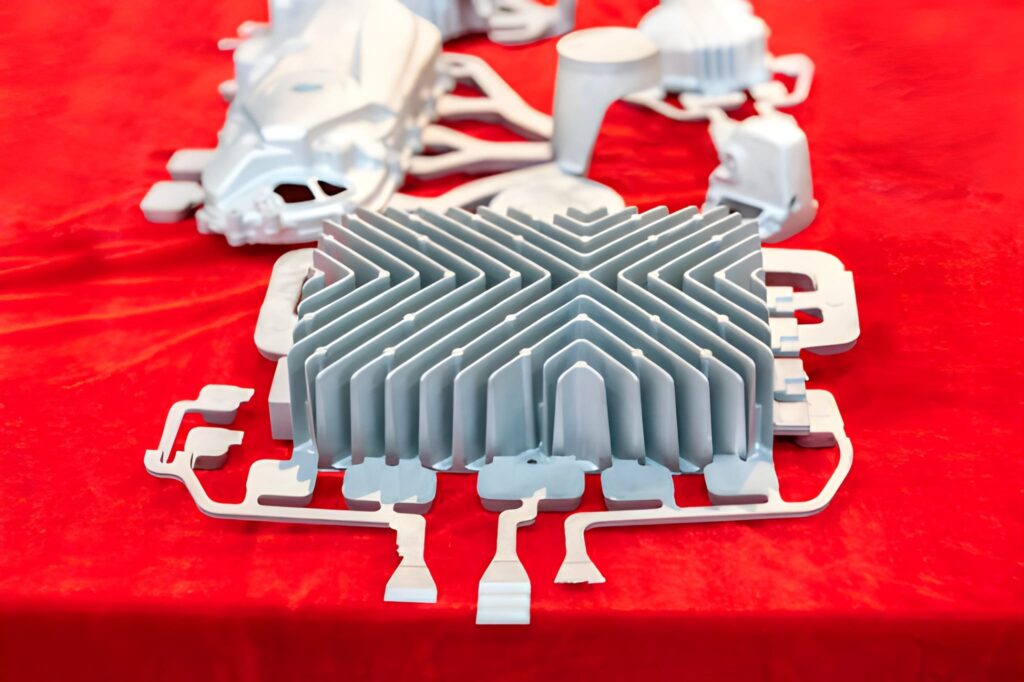
Heat sink with gate runner system and riser casting parts, aluminum alloy
Die casting is a process that requires the melting of aluminum and pouring it into a pressurized steel mold. The technique can be used with complicated shapes, such as thick bases or angled fins, difficult to extrude. When the mold has cooled, the heat sinks are taken out of the mold and edges machined to exacting tolerances. The Automotive or high-performance electronics is also common with this technique.
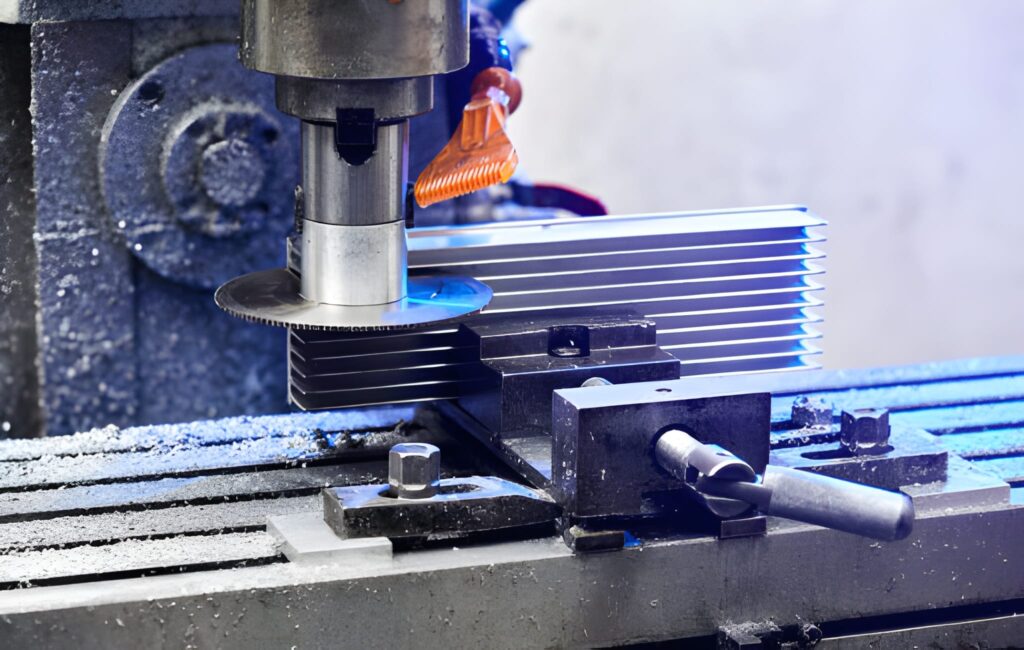

Aluminum Heat Sinking Machining
CNC machining starts with a solid block of aluminum. Cutting tools cut fins, slots, and holes in the mounting as per specific CAD designs. This process is slower than extrusion or casting and permits custom shapes, bizarre fin spacing, or prototypes. It is commonly applied to low-volume or high-precision heat sinks, whereby the usual techniques are not able to produce the needed design.
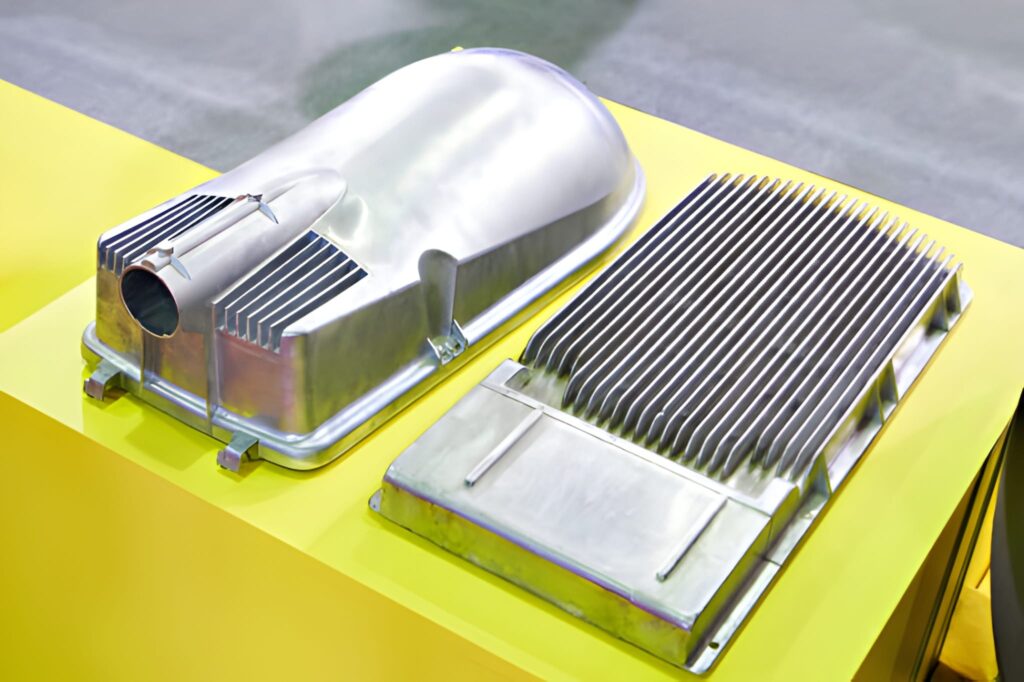

Aluminum Stamped Heat Sinks
Presses can be used to stamp fin shapes using thin aluminum sheets at high speed. The fins are then attached to a solid aluminum base with thermal adhesive, solder, or pressure bonding. The method can be applied to small-scale devices such as LED modules or small-scale electronics, where a small number of thin fins are required to operate effectively in heat dissipation.
The completeness of aluminum heat sinks is significant in that it safeguards the metal and is even able to enhance its ability to conduct heat. The proper finish can be determined by the location where the heat sink is to be utilized and its behavior with other parts.
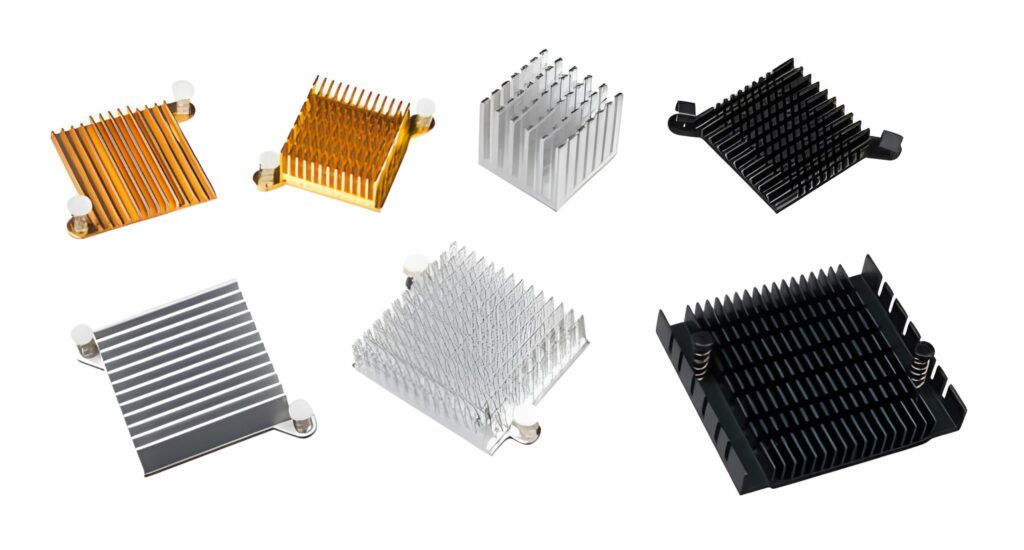

Set of Various Anodized Aluminum Coolers
Anodizing produces a coating of aluminum on the surface, which is thin and hard. This coating keeps the heat sink rust-free and wear-free. Anodized is used as an example of heat sinks in outdoor equipment or electronics that are subject to moisture. It does not harm the metal because it keeps it working longer.
Powder coating gives a coating that is more protective and may turn the heat sink color. This is applicable in components that are inaccessible or frequently touched, such as in computers or automobile panels. It eliminates scratches, lessens corrosion, and eases the cleaning process.
The heat sinks are smoothed by polishing. A smooth and flat surface makes the heat sink contact more with the chips or components, and so enhances heat transfer. This is particularly significant to CPUs, GPUs, or power modules, where every degree of heat counts.
Making the surface a little rougher, as sandblasting does, may seem to be the last thing you want to do with polishing, but it assists the coating in adhering to the surface. It is also applicable to the heat sinks in industrial or automotive applications where dust or rough environments are encountered by the parts.
Other finishes are aimed at preparing the surface to be used as the thermal paste or pads. The paste is spread evenly and conducts heat efficiently because of its smooth and flat surface. The preparation of such surfaces is often done by machining, polishing, or light anodizing.
In the production of aluminum heat sinks, a number of feasible factors directly affect the performance and efficiency. These are what you have to check first before production in order to avoid an expensive error.
Not every aluminum alloy is the same. 6063 and 6061 are popular due to the fact that they are good conductors of heat and are easy to machine. The option to use a lower-grade aluminum will initially be cheaper, but will reduce the heat dissipation, which will affect the component it cools.
A critical consideration is the fin spacing, height, and thickness. Excessively thin fins can bend during machining, and too small spacing can trap air and lower the cooling efficiency. The design should be compatible with the manufacturing process, be it extrusion, milling, or die casting, to produce reproducible results.
Thermal resistance can be produced by even minor variations in the flatness of the bases or the perfection of the alignment of the fins. Keep the base plate and fin modifications tight to be in contact with the electronic component. When it is not aligned, then it will perform badly, or it will involve a lot of rework.
Thermal transfer is influenced by surface roughness. Even contact with thermal pads or paste is enhanced by a smooth base, and corrosion resistance is provided by anodizing. Decide on coating, depending on thermal and environmental conditions.
The holes, slots, or clips used to mount heat sinks must be precise. Components may be stressed or thermal performance may be compromised, or make parts difficult to assemble because they do not fit properly on the mount. Before your component is manufactured, verify these features.
Select a quantity-based manufacturing method. Standard profiles are more quickly and cheaply extruded, and small batches or custom designs are better done by CNC milling, whereas high-volume production is well handled by die casting. The trade-off in cost and efficiency makes the process viable.
Arrange dimensional inspection, thermal performance tests, and surface checks. Any omission of these may lead to heat sinks that fail to achieve the requirements of performance, thus a waste of material and time.
Aluminum heat sinks are used wherever electronics or machinery generate heat that needs to be controlled. They assist in ensuring performance and avoiding damage by moving the heat out of the critical components.
Electronic equipment such as power transistors, voltage regulators, and inverters emits a lot of heat. These components are fitted with aluminum heat sinks that directly attach to the components to maintain the temperature below the safe levels to guarantee safe functioning and high durability.
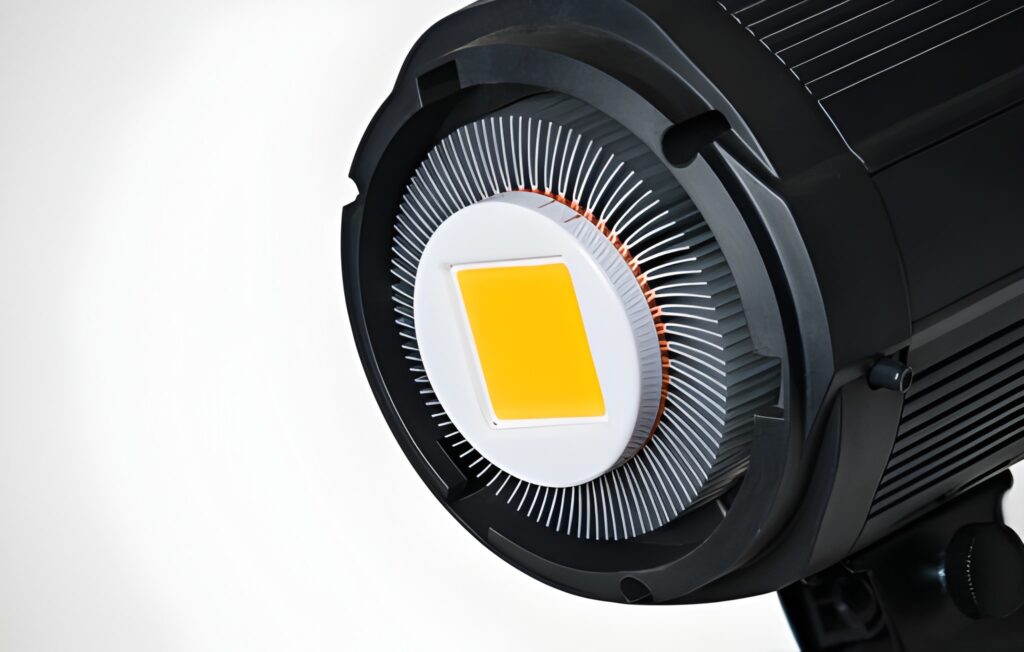

Yellow LED module in a photographic reflector with aluminum cooling fins
Powerful LEDs produce heat, and inflation can be brighter or fail. Heat sinks help to extract the heat in the LED chips and ensure efficiency and stability of color, and prolong the life of the lighting unit.
Computers and servers generate high heat in their CPU, GPUs, and memory modules. Aluminum heat sinks offer efficient cooling and are sometimes used with fans as a cooling method in order to avoid thermal throttling and provide stable performance at high workloads.
Industrial equipment development may have motors, drivers, and control units that operate continuously and generate heat. These components are cooled using aluminum heat sinks, which ensure the smooth running of machines and minimize downtime due to overheating.
In electric and hybrid car systems, and in the infotainment and safety systems, modern vehicles include power electronics. Heat sinks are used to control the temperatures of engine control units, LED headlights, and battery management systems, which are reliable on the road.
Conversion of energy is accompanied by heat generation in solar inverters, wind turbine controllers, and other renewable energy electronics. Aluminum heat sinks ensure efficiency and overcome overheating in hard outdoor conditions.
At ApexRapid, we make aluminum heat sinks that fit your exact needs. Our team helps you pick the right size, shape, and finish so your electronics, machines, or automotive parts stay cool and work efficiently. We use high-quality aluminum and offer different alloys depending on how much heat you need to manage and how strong or light the part should be.
We focus on quality at every step. Our ISO 9001-certified process ensures each heat sink is precise, durable, and performs well. We also provide anodizing, powder coating, and other surface finishes to prevent corrosion and improve heat transfer.
With ApexRapid, you get fast turnaround, practical advice, and custom designs that integrate smoothly into your projects. We make sure your heat sinks are ready to go, saving you time and reducing waste.
How do I choose the right aluminum heat sink for my device?
You should consider the power output, operating temperature, and size limitations of your device. The heat sink should match the thermal load and allow proper airflow to prevent overheating.
Can aluminum heat sinks be used in high-temperature environments?
Yes, aluminum has good thermal conductivity and is lightweight. For very high temperatures, surface treatments or additional cooling, like fans, can be applied to improve performance.
What is the typical lead time for custom aluminum heat sinks?
At ApexRapid, we can produce custom aluminum heat sinks in as fast as 2 to 5 days, depending on complexity. We also provide prototyping and rapid production options to meet urgent project timelines.
