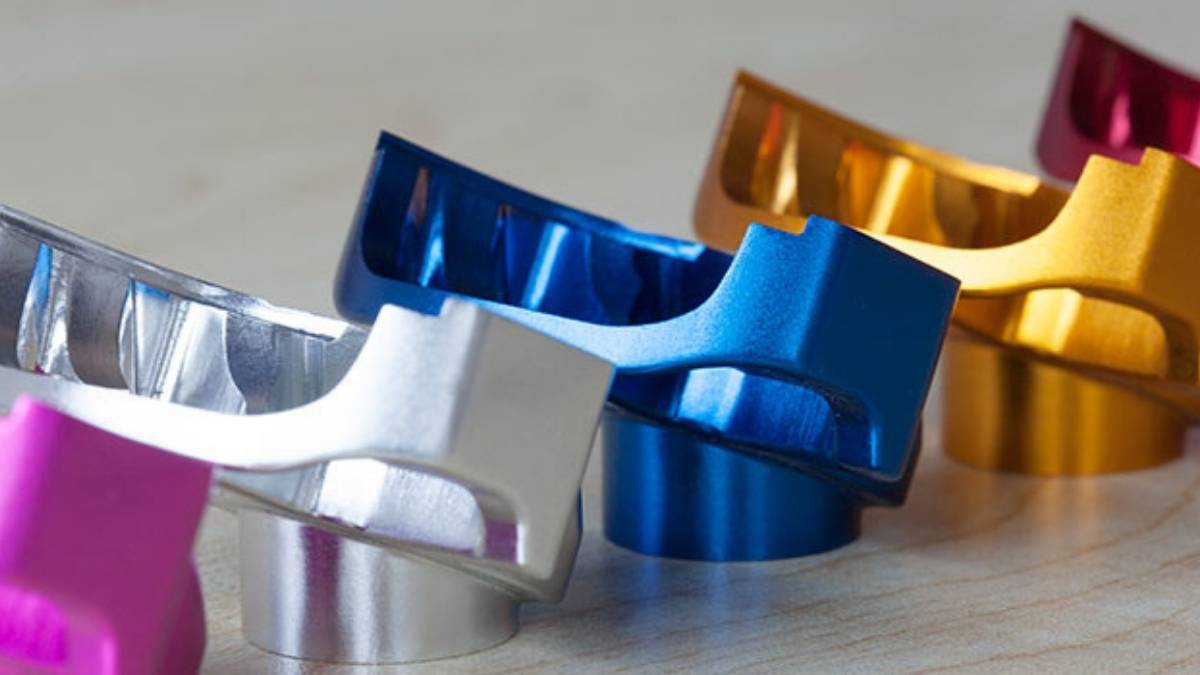
Aluminum Anodizing is a protective enhancement process that aids aluminum’s durability. It creates a thick, protective oxide layer on its surface. The treatment improves corrosion resistance and also adds aesthetic value to aluminum parts. It’s widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and architecture.
The anodizing process makes aluminum stronger and more resistant to wear. It also allows for vibrant colors, perfect for design purposes. Aluminum anodizing not only improves performance but also extends the material's lifespan. This guide will walk you through the anodizing process, benefits, and key applications.
Aluminum anodizing strengthens aluminum products and improves their surface aesthetics. The surface acquires additional protection through this process because its oxide layer thickens to resist corrosion and prevent scratches and wear. It finds its best use when dealing with strong materials needed in aerospace and automotive fields and construction projects. The best part? Since these oxide layers remain a fundamental component of the aluminum they will not detach like conventional coating layers would.
The standout advantage of anodizing involves the ability to introduce different colors into materials without compromising their structural integrity. The wide selection of different colorful options enables aluminum to acquire both attractive aesthetics and an enhanced barrier against harmful UV rays. You can achieve functional performance and an attractive finish with anodizing since it gives you the best of both worlds.
Anodizing operates as an eco-friendly production process. It happens without chemical contaminants and generates low waste levels during the operation. An anodized product delivers a durable output that maintains environmental sensitivity. Anodized aluminum serves as an excellent selection if you want to increase aluminum part durability alongside performance capabilities and aesthetic appeal.
Let’s look at the steps involved in the Aluminum Anodizing process.
To start the aluminum anodizing process you must first cleanse the aluminum part surface. The removal process eliminates all traces of dirt, grease, and oxide from its surface. The surface needs to be entirely clean to allow a successful anodizing process attachment. Cleaning solutions, acids, are usually used, and serve as preparation agents to remove contaminants. So, these make the part suitable for anodizing.
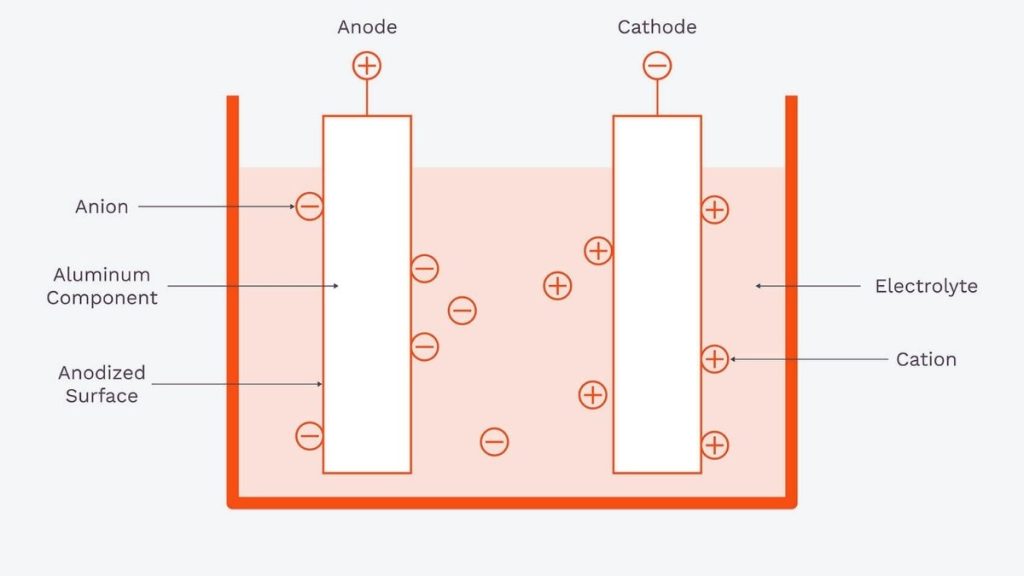
After cleaning the aluminum, it goes through an electrolyte bath encompassing sulfuric acid. Here, the anodizing operations start. During the electrochemical reaction, the aluminum section functions as the anodic part. An electrical current running through the electrolyte bath enables aluminum to react with acid to create a dense oxide coating on the aluminum surface.
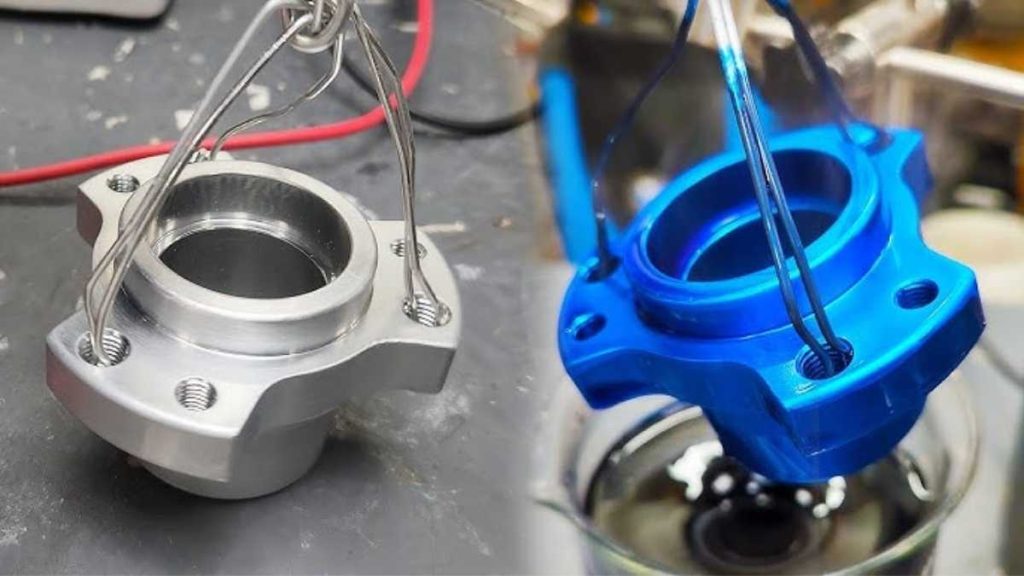

An electrical current activates aluminum atom oxidation to establish oxygen molecule bonds with the metal structure. The intended layer on the aluminum surface stabilizes through this process. The oxide layer developed serves as superior protection against several forms of degradation, including corrosion and wear, as well as environmental damage. The oxide layer forms based on the temperature, current control, and time spent in the bath.
The distinctive advantage of anodizing involves adding color to aluminum surfaces. The aluminum material becomes ready for dyeing following the formation of the oxide layer. The layer pores accept dye molecules, which produce bright color effects. Due to its protection mechanism, the color remains durable and does not easily fade away. The coloring step can be omitted to preserve the aluminum's natural appearance.
The last operation in anodized aluminum production is the sealing process. Hot water immersion or a sealing solution application serves to close the pores within the oxide layer of the aluminum part. It protects the part from corrosion and prevents stains on finished aluminum surfaces. Sealing forms a protective barrier. It maintains the applied color and keeps it bright for an extended duration.
The most frequently used types of anodizing are;
Chromic acid anodizing creates a delicate coating. It uses an electrolytic bath containing weak acid substances. The process yields a thinner oxide layer than Type 1. It provides outstanding protection from corrosion, which makes it suitable for aircraft and military needs that require lightweight, durable parts.
However, like other options of anodizing, chromic acid anodizing is limited or unable to create colorful effects. It protects structures from damage while preserving their strength properties. Therefore, it is suitable for materials needing strength and environmental protection characteristics.

The most frequently used method for anodizing processes is sulfuric acid anodizing. It forms a powerful oxide coating that protects it against damage. The porous oxide layer lets aluminum absorb dyes for different colors.
The surface hardness and wear resistance properties of Type II anodizing are recognized for their quality. The process serves the automotive sector and consumer electronics industry, and architectural applications. Designers select Type II anodizing for decorative finishes as they have the option to polish and color the finish. The material proves to be economical and enduring particularly when employed for demanding conditions.

Hard Coat Anodizing is an advanced technique used in the modern manufacturing industry. It gives higher durability and a denser oxide layer. It produces a firm, dense top layer that shields against abrasion, together with chemical decay and surface marks.
On the application side, it works best for components subjected to demanding usage, like mechanical gears and hydraulic system cylinders. The high-performance components within aerospace defense and manufacturing industries make use of Type III anodizing. It’s relatively expensive from other options, and usually comes with limited color options when compared to Type II.

As the name implies, the type allows the coloring process of aluminum materials by using organic dyes. The anodizing process ends with aluminum being dyed within its pores to form permanent bright finishes.
The process results in vivid colors. These last for a long period. Consumers find organic dye anodizing optimal for automotive, electronics, and consumer products. Moreover, organic dye anodizing aids in improving aesthetic qualities that serve practical functions.
Here’s a table comparing the different types of aluminum anodizing processes based on key factors:
| Anodizing Type | Electrolyte Used | Oxide Layer Thickness | Durability | Corrosion Resistance | Color Options | Applications | Cost & Complexity |
| Type I - Chromic Acid Anodizing | Chromic acid | Thin (0.0001 to 0.0003 inches) | Moderate | High | Limited (natural finish) | Aerospace, military, and electrical parts | Moderate cost and complexity |
| Type II - Sulfuric Acid Anodizing | Sulfuric acid | Moderate (0.0002 to 0.001 inches) | High | Very High | Wide range (dyeable) | Automotive, architecture, and consumer electronics | Affordable and common process |
| Type III - Hard Coat Anodizing | Sulfuric acid (extended time) | Thick (0.001 to 0.002 inches or more) | Very High | Very High | Limited (dyeable, darker colors) | Aerospace, defense, heavy-duty machinery | High cost and complex |
| Organic Dye Anodizing | Organic dyes (post-anodizing) | Depends on base anodizing (Type II or III) | Moderate | High | Wide range (vibrant colors) | Automotive, consumer products, decorative parts | Moderate cost, additional step |
Table Description: The table above provides a side-by-side comparison of the different anodizing types. It outlines their key technical aspects. So, you can choose the right process for specific applications.
Here are some common benefits and limitations of aluminum anodizing.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Protects aluminum from rust and damage. | Fewer color choices than other finishes. |
| Makes aluminum harder and more scratch-resistant. | The anodizing layer can slightly change the part size. |
| Available in various colors and finishes. | Hard coat anodizing can be expensive. |
| Uses non-toxic processes and materials. | Some types of anodizing require special equipment. |
| Lasts longer under wear and tear. | Hard to fix if damaged. |
| Ideal for electrical components. | Only works on aluminum materials. |
| Offers better protection against high temperatures. | Requires specific machines and expertise. |
Here’s a list of aluminum alloy types commonly used for anodizing:
Here are the common industries benefiting from aluminum anodizing;
Anodization provides aerospace parts protection against corrosion damage. It applies to engine components and aircraft frames for long serviceability. The procedure maintains aluminum components weightless yet durable for demanding applications.
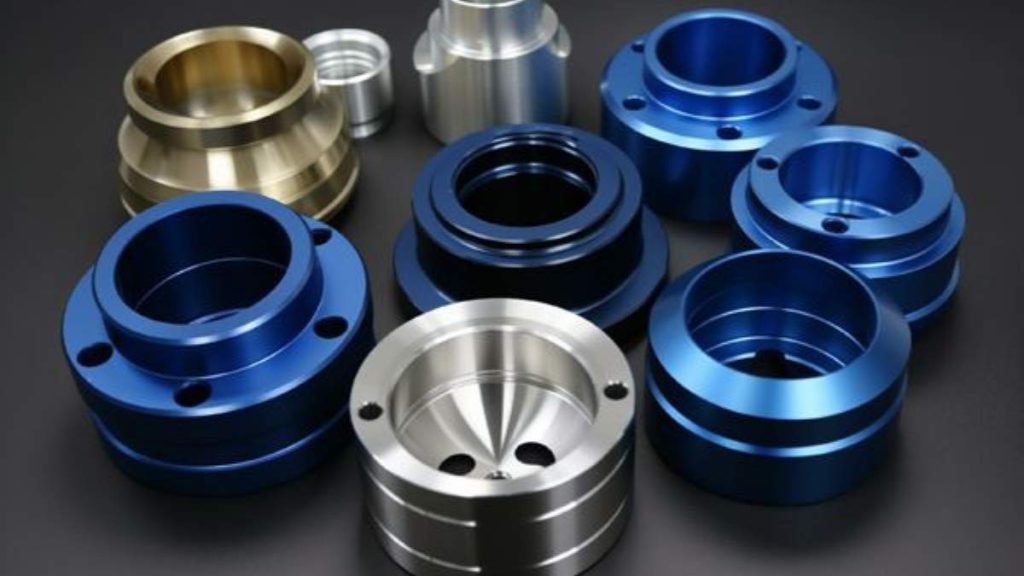

Automakers usually employ anodized aluminum for manufacturing wheels and trim sections and enhance their durability traits. Anodization protects parts and defends against both UV rays and corrosive substances. Manufacturers have the flexibility to choose from vibrant colors to achieve design flexibility through the anodizing process.

Electronic products use anodized aluminum as a protective measure. It works as an effective protective shield that safeguards mobile phones and laptops against surface damage. Moreover, it allows the production of aluminum components with various coloring effects and surface appearances.

Architects use anodized aluminum in window frames and wall structures. It protects buildings against corrosion, in addition to increasing material durability. The process works optimally for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Anodized aluminum safeguards components used in boats, such as hulls and props. It maintains high strength while safeguarding against saltwater harm. The process ensures that it is critical for components facing aggressive marine conditions.
Anodizing helps maintain the effectiveness of medical devices and tools. It increases durability and makes products more maintainable for cleaning purposes. Besides, it allows material resistance against bodily fluids and ensures protective measures.

Sports equipment usually uses aluminum anodized treatment. Particularly, it applies to aluminum-made components of bicycles and golf clubs. Moreover, it produces strong yet light gear equipment. Anodized finishes work to defend equipment against severe damage.

The additional durability of gears and valves in machinery comes from an anodization process. Anodizing provides equipment with a defense against wear and corrosion. In addition, it provides dependable service in tough industrial applications.
Anodized aluminum is preferably used in signs and plaques. It supplies lasting protection and is available in vibrant coloring options. Anodizing products can retain their excellent appearance while extending their service life.
The cost of anodizing aluminum depends on factors like the alloy, finish, and part size. On average, the costs range from $0.10 to $0.30 per square inch. Custom colors or thicker layers may increase the price. For a more accurate estimate, it's best to request a quote from our experts based on your specific requirements.
Here are some practical tips used for choosing aluminum anodizing;
Not all aluminum alloys respond well to anodizing processes. You can consider alloys from the 6000 series for anodizing. These offer good functional benefits and deliver smooth, durable finishes. So, first, you need to verify what alloy matches your precise requirements.
Anodizing usually gives these finishes, like transparent, dull, and tinted finishes. The anodized layer must be thicker to protect parts when they will experience rough environmental circumstances. The selection of a vibrant finish is ideal for decorating items.
Anodizing protects aluminum parts from saltwater damage and extreme weather conditions. You should consider the environment where your parts will be used to select the best finish and thickness.
Anodizing treatment creates a surface coating that leads to minor dimensional changes in your parts. Generally, for small-sized parts, you need to consider the dimensional shift caused by anodizing. As these parts need high detailing and precision.
Aluminum anodizing increases the product's durability, appearance, and corrosion resistance. This makes it ideal for a variety of industries, from automotive to aircraft use components. By choosing the right alloy, finish, and considering environmental factors, you can get the best results from anodizing. However, remember to plan for slight changes in part dimensions and make sure the anodizing process fits your needs for both function and look.
1.What are the main benefits of anodizing aluminum?
Anodizing improves corrosion resistance. It strengthens the aluminum and allows for colorful finishes.
2.Can anodized aluminum be repaired if damaged?
Repairing anodized aluminum can be difficult. If damaged, parts may need to be re-anodized to restore their protective layer.
3.Does anodizing affect the size of the aluminum part?
Yes, anodizing adds a thin layer to the surface, which can slightly increase the part's size.
4.Is anodizing safe for the environment?
Yes, anodizing is eco-friendly. It uses non-toxic chemicals and creates little waste, making it a sustainable finishing option.
