You might process or fabricate tough metals every day at machining shops. But Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) machining brings significant challenges. This titanium alloy is strong, lightweight, and highly resistant. It’s perfect for aircraft use, medical devices, and defense parts. But it doesn’t behave like aluminum or steel.
Moreover, grade 5 holds heat near the tool's cutting zone. That heat shortens tool life and dulls the edge quickly. If you don’t adjust speeds, you’ll break tools fast. Traditional machining methods won’t deliver the clean results you desire. That’s why titanium needs a smarter approach.
You must use sharp tools and slow cutting speeds. Flood coolant or high-pressure systems are essential here. Even a small mistake leads to chatter, burrs, or failure. You want smooth chips and stable cuts every time. That takes control, not force.
This article shows you how to machine titanium well. You’ll learn how to manage heat and tool wear. You’ll also discover proven strategies to improve your results. If you work with Grade 5, these tips will help you succeed.

Titanium Grade 5
Ti-6Al-4V, another name for Titanium Grade 5. It is a popular and highly used titanium alloy these days. It is composed of titanium, with a smidgen of aluminum and vanadium, making up 6% and 4% of the composition. Because of this blend, the alloy is strong, light, and durable.
Since it has greater strength and less weight than pure titanium, this grade is often used in aerospace, medicine, car making, and similar engineering areas. Moreover, it is resistant to corrosion and high temperatures, it can handle difficult working conditions.
However, machining Titanium Grade 5 is difficult to do. Since the metal is very strong and conducts heat poorly, machining tools need to be handled carefully to preserve their sharpness and avoid errors. To create high-quality parts, you should understand the traits of this alloy.
Overall, Ti-6Al-4V is known for its strong mechanical properties and the ability to function well in various tough situations.
Before machining, you should know what makes Grade 5 unique. This alloy does not act like steel or aluminum. It’s able to support a heavy load, but is tricky to cut. Success in machining is determined by how well you control its features.
Compared to other grades, Grade 5 titanium is strong and resistant to heat. Still, these same qualities lead to many tough situations. There are details below that describe the value of this material to machinists.

Titanium Grade 5 Products
Titanium Grade 5 is very strong and is also lightweight. It is possible to make rigid parts that remain small. Hence, it is commonly used in parts for planes, medical tools, and racing equipment.
As a result, your tools will undergo more stress. To manage the car, use firm settings and slow down the food input.
Titanium has low thermal conductivity. The heat leaves only on the side of the edge. If you fail to cool your tools after use, they may wear out soon.
While machining, always rely on flood coolant or air blasts. Therefore, your inserts could get damaged in the middle of a cut.
Titanium becomes harder during the machining process. In other words, difficulties are rising for your tools. Sharp tools are better to use than those with dull blades. The cutter should enter the grooves and then pull out easily.
Titanium can return to its original shape after being machined. An object made of rubber doesn’t keep its form once it is released. As a result, hitting the required limits is a bigger challenge.
Therefore, allow enough for the spring-back in the structure as you finish cutting them.
Titanium reacts promptly to high temperatures. Sometimes, it may stick to the tool, melt to it, or leave marks on your workpiece. Such behavior marks the tools and changes the appearance of the parts.
Applying a coating to your tools and cooling them prevents the mix from sticking. Try not to keep the tool in one place for too long.

Machining Titanium
You can’t work with common tools on machining titanium grade 5. Tools used to cut titanium must be able to withstand high temperatures. Use carbide for your job, as they are made for intense stress. Using sharp edges will ensure that the parts do not rub against each other.
Ensure the structure of your models uses firm shapes. Go for end mills that have a high number of turns and a small number of flutes. More flutes allow chips to be cleared better and make cutting easier for them. It keeps the area the smoker is using cooler.
The use of coatings can change the outcome of machining titanium. To achieve the best outcomes, use tools coated with TiAlN or AlTiN. They keep heat from the tool and lengthen the life of the tool. Avoid using tools without a coating, since they will not last long.
When using shorter tools, vibration is lowered, and the tool will last longer. A slight movement in your tools can create imperfections on your part. Having the proper setup validates that your work is orderly and repetitive.
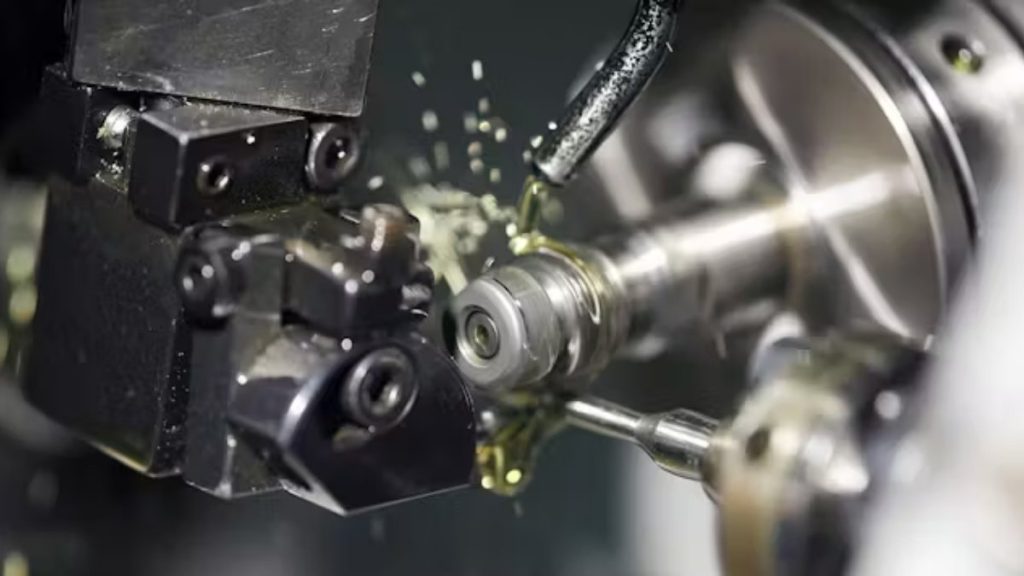

Lubrication For Titanium Machining Operation
Titanium has a good ability to retain heat. Since heat burns fast, be sure to manage it properly. A high-pressure coolant must be used all the time. This action removes the chips and cools the part that is being cut.
Remember not to apply the paint randomly. Ensure the coolant is directed onto the point of the tool you are using. It creates less friction, and chips are easily broken. Reducing the temperature of the job allows the tools to last longer and provides better results.
For cutting titanium, use fluids that are oil-based or emulsions. They grease the tool and stop the formation of thick edges. They also prevent heat cracks from appearing on your part.
Ensure the coolant circulates throughout the whole process. If you use the stop-and-go method, the temperatures will rise faster than you intend. When tools are held at a constant lower temperature, results stay the same.
Titanium is cut differently from steel. You have to use different feeds and speeds than usual. Because the material is strong and poorly conducts heat, the machine is set differently. Avoiding tool wear and rough surface finishes can be done by choosing the best parameters.
Begin with trials on a small scale and monitor their success. Ensuring a stable setup and the right settings leads to reduced scrap and time when your printer is not working.
Use a speed between 60 and 90 meters per minute, as going faster will cause the tool to overheat and die. Traveling slower can help you maintain the sharpness of your tools and prevent your chips from flying everywhere. Since titanium responds to heat very slowly, you should cut it steadily.
Pick tools coated in carbide that can handle high temperatures. They remain in good condition for a long time and handle less friction at the spot where they contact the road.
Start by using a feed that is less than 0.1 mm per tooth. Working with titanium is difficult because it won’t allow you to force the cut. When you lower your feed rate, the cutter will engage without making any noise.
Only after the setup is stable can you add some steps at a time. Titanium is always more stable than fast.
Try to avoid wearing dresses that have large, wide necks. Titanium increases the pressure rapidly. Try to keep the cut depth below 3 mm whenever you are finishing the piece.
Ensure to put on light layers when you finish the sculpture. This results in improved accuracy of the pieces produced. A step with low depth aids in the chip shape and reduces too much heat.
You may find out that your titanium wears your tools. Unmanaged coated tools will only last a short period. Verify the number of passes, the duration it takes, and the loudness of the process. Any abrupt changes, such as a decrease, could show dulling.
Swap out your equipment before it starts to malfunction. Do not try to overdo things. Using worn tools causes the tool and the piece to shake. A clean line will always result in a better picture.
You should make use of effective tools for Grade 5 titanium. Some cutters are unable to manage the strong and hot material. A bad tool will burn up and damage whatever you are working on. Choose the right tools before getting your hands on the work material.
The process of machining titanium requires accuracy, and being ability to resist wear. An outcome depends on the geometry, material, and coatings used. The section is intended to guide you in finding high-quality tools that last longer.
Tools made of carbides are most effective when machining titanium alloys. They can withstand heat and pressure. Pick end mills or drills that are strong at the shank and sharp on their edges.
Carbide is preferred over HSS when dealing with hard materials. There will be more areas you can probably cut with one tool, and the finishes will be smoother.
Pick tools that have a high angle on the razor-sharp edge. They help decrease the pressure and lead to better movement of the chips. Having narrow flutes will help you remove waste chips quickly.
Opt for short tools so that the steel is not bent when you hammer it. Accurate and well-made tools do not vibrate much as they are loaded.
Whenever you work with titanium, choose PVD-coated tools. TiAlN or AlTiN helps protect the cutting tool and reduce friction. Using coatings helps shield the car from wear and heat.
An item with a coated surface cuts better and lasts longer. Fewer replacements and fewer shocks.
Do not apply worn-out tools to anything made from titanium. A blunt edge can damage the wood's finish, chip the tool, or bend the part.
Before anything else, sharpen the cutter you will be using. If a tool is worn, change it before it leads to damage to a precise part.
Titanium Grade 5 is a unique material, so it must be machined with additional care. It is very strong, poor at passing heat, and hardens when worked, so using standard machining is not effective. When you use the right techniques, the tool lasts longer, produces a smoother finish, and works better.
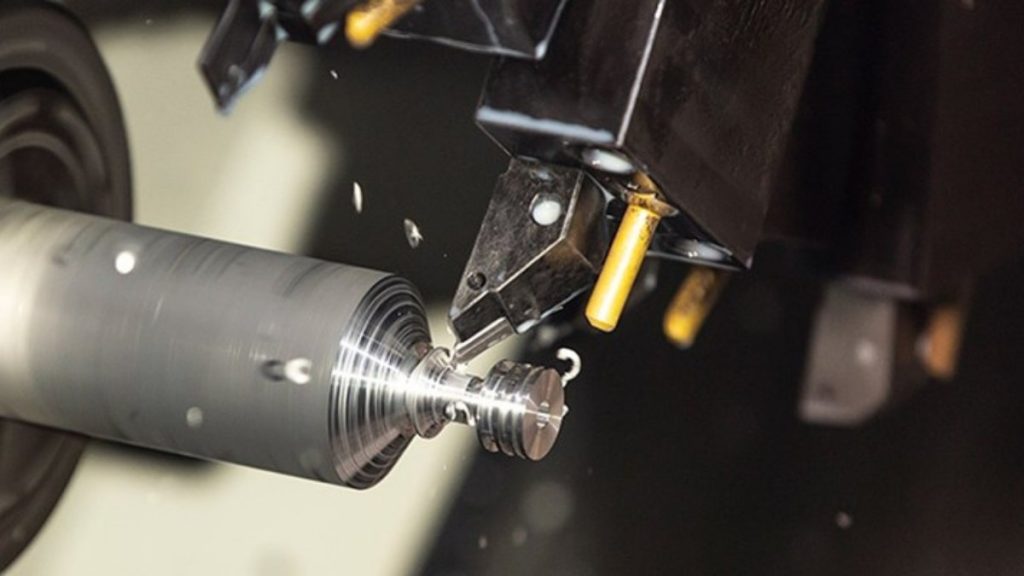
Titanium CNC Turning
Titanium Grade 5 is often shaped using the process of turning. Sharp tools with a positive rake angle use less effort to cut the material. If you cut quickly and feed at a moderate rate, both the chips are removed smoothly and the tool’s temperature is controlled. Coolant helps significantly during turning by reducing the heat generated.
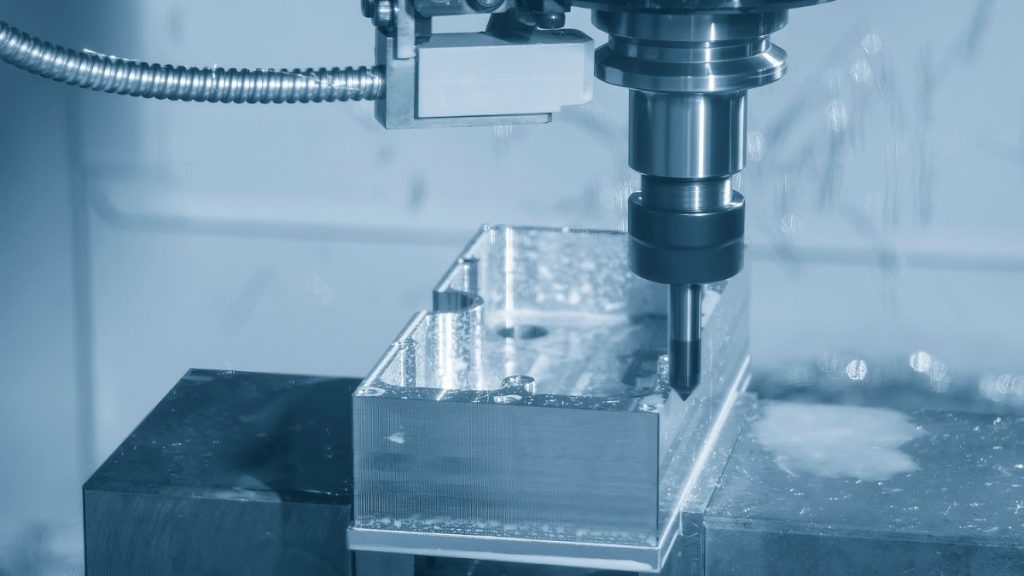

Titanium CNC Milling
To process titanium alloys on a milling machine, precision with speed and feed is required. End mills typically made of carbide or coated tools, like TiAlN-coated cutters, provide high durability. High-pressure coolant systems evacuate chips and keep the cutting area cool. When you cut in a steady manner, the problem of work hardening is reduced, and your tools wear less.
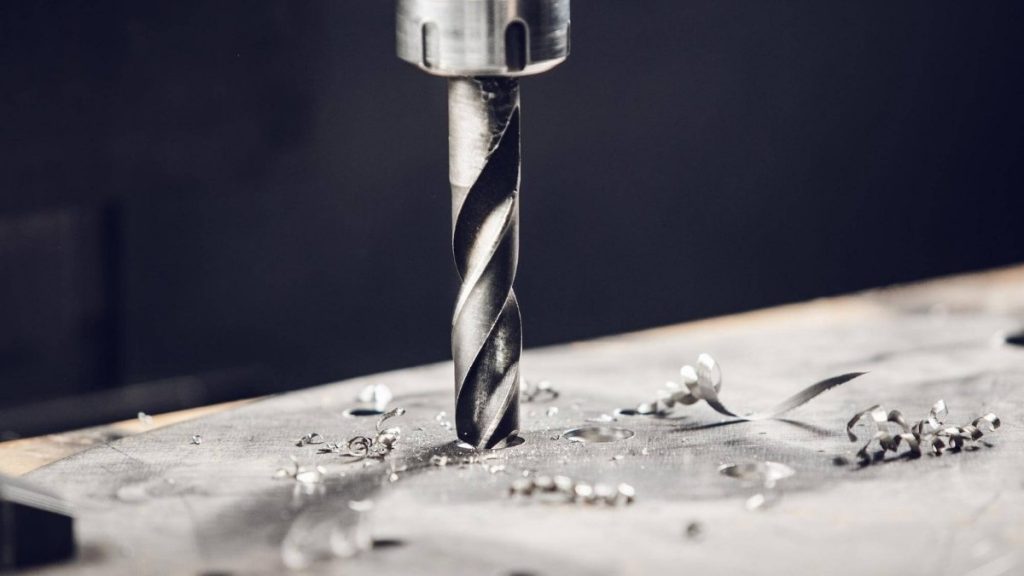

Drilling Titanium
As Titanium Grade 5 is hard to drill, you need split-point geometry drill bits. As a result of this design, the gun requires less power and is more accurate. With peck drilling, the drill moves back every so often to clean out the chips. A slower spindle and rapid tool feeds will produce less heat and lengthen the life of your tools.
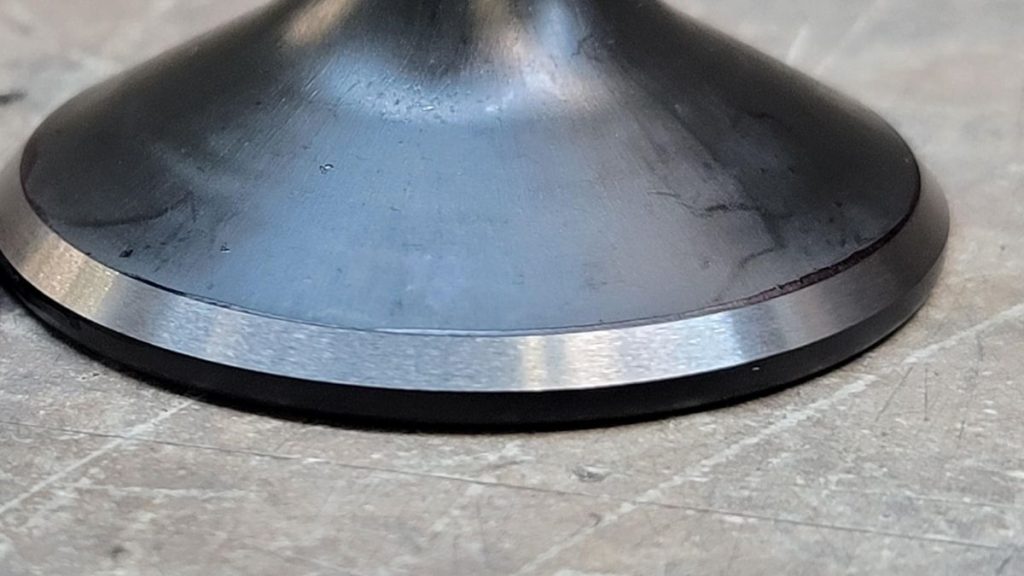

Titanium Grind Machined Part
Titanium Grade 5 machines are often ground to validate that the products are extremely precise and have smooth surfaces. These wheels are recommended as they remain sharp and avoid clogging. Coolant should always be applied to the titanium to prevent it from overheating.
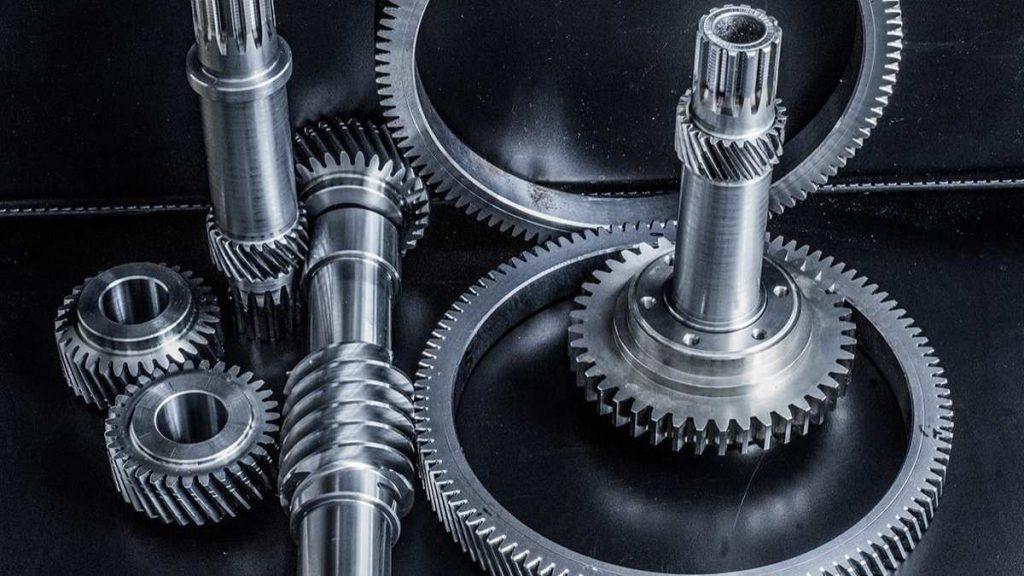

EDM Machined Titanium Parts
EDM makes it possible to machine places that are either tricky or difficult to reach without touching them. Using sparks of electricity, this process can make very precise cuts without applying any mechanical force. EDM ensures that small, intricate titanium parts remain undistorted.
There are significant challenges involved during Titanium Grade 5 machining. Knowing these issues helps you decide on the best ways to deal with them. Let’s study the common challenges and see how they disrupt the machining process.
Grade 5 titanium does not transfer heat effectively while being worked on during machining. As a result, heat gathers on the cutting tool and the material it is cutting. Extreme heat may cause your tools to deteriorate and be damaged. It is vital to use high-pressure coolants and adjust the cutting speed accordingly.
Work-hardening in Ti-6Al-4V occurs rapidly. If the material becomes stressed during cutting, its surface becomes harder, and it is more difficult to cut further. This means the bit gets dull faster and also requires more power. Work hardening can be minimized by using sharp blades by making just one cut instead of many.
Due to its hardness and rough texture, Titanium Grade 5 tends to cause tools to wear out quicker. Regular carbide tools are used, but they still may become dull fast unless the right cutting conditions are met. If a tool is treated with TiAlN or diamond-like carbon, its life is likely to be longer. To ensure quality, tools must be frequently checked and replaced when needed.
Titanium chips tend to wrap around the tools and machines being used. Using chip breakers, reducing the feed rate, and adjusting the coolant flow help chop the chips into smaller bits.
For machining titanium 5, the setup should be sturdy and immovable. When these tools shake or bend, it may result in a rough surface and could even break them. Risks are reduced by using heavy-duty machines with holders that are maintained regularly and kept in good condition. For machines to function smoothly, they must be well-maintained.
Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is a widely used alloy. It is known for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. It’s popular across the aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. However, machining it effectively requires special care and knowledge. The alloy’s unique physical and chemical features, such as low thermal conductivity and high strength, present distinct challenges during machining.
Proper machining of Titanium Grade 5 involves understanding its behavior under cutting conditions. Its poor heat dissipation demands the use of effective cooling methods to prevent tool damage. Additionally, the material’s tendency to work-harden quickly means sharp tools and optimized cutting parameters are necessary to maintain efficiency and prolong tool life.
Machining this alloy also involves dealing with fast tool wear, chip control issues, and strict machine rigidity requirements. Carbide tools with advanced coatings are the preferred choice, while controlling chip formation improves safety and machining flow. Maintaining machine stability reduces vibration-related defects and improves surface finish quality.
By recognizing these factors and applying best practices such as selecting the right tooling, adjusting speeds and feeds, and using high-pressure cooling, you can achieve precise, efficient machining of Titanium Grade 5. This ensures the production of high-quality components while optimizing operational costs and tool lifespan.
In summary, machining Titanium Grade 5 demands technical skill, proper equipment, and continuous attention to detail. When done correctly, it unlocks the alloy’s full potential in demanding applications, making it a valuable material for modern manufacturing.
