You’ve likely seen CNC machines in action somewhere. They carve, cut, drill, and shape, without blinking. From aerospace to woodshops, they’re silently transforming industries.
Today’s factories don’t rely on manual control anymore. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines run the show now. With precision at their core, they reduce human error to nearly zero.
But here’s where it gets interesting—you’ve got options. Different CNC machines do different things. Each one has its niche, and the impact is global. Let’s break down what makes each type valuable and how they’re reshaping how we build everything.

Many people ask—what exactly is a CNC machine? It is a tool driven by a computer. It gets instructions that it transforms into actions to move, cut, and shape the material.
You don’t have to watch it every step of the way and direct it. Supply the design with data, and it handles the processing. This is the advantage of using automation with accuracy.
These machines move fast because they have been given pre-set programs. They work things out mathematically rather than guessing. They can work with plastic, metal, or wood without difficulty.
Many industries benefit from using CNC machines, which cause fewer errors. The global number of CNC machines went up by 7.3% in 2024. Return on investment can be tracked, so companies are investing greater sums.
Materials science is part of manufacturing in the automotive, aerospace, and healthcare industries as well. They are now needed, instead of being considered optional. The period of shaping done by hand? That is no longer happening now.
You don’t need to lift a tool manually. CNC machines follow a digital blueprint. Each step is executed with absolute precision and no guesswork.
From coding to cutting, here’s how it all unfolds. You’ll see why these machines changed production forever.

A digital model is the base for everything else. CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used by engineers. It creates a detailed drawing for the product, whether viewed from the side (2D) or different sides (3D).
Each line, curve, and shadow is up to your choice here. The machine is not able to move without the blueprint. CAD models give robots and machines instructions.
The software packages for this are AutoCAD and Fusion 360. No matter where you are, companies rely on these to draft well. Making a mistake anywhere will affect all the data being processed.
After that, the CAD file is changed into a language that the CNC machine can use. CAM software is responsible for changing the CAD (Computer-Aided Design) information into data needed for actual manufacturing. It takes design and generates G-code from it.
G-code might be compared to machine language. It directs the machine regarding how speedy it should operate. It also affects how deep the groove is going to be.
Most of the work on this stage is handled by Mastercam or SolidCAM. They find the best way to do things, use fewer resources, and speed up the process. If the code is better, production will be faster.
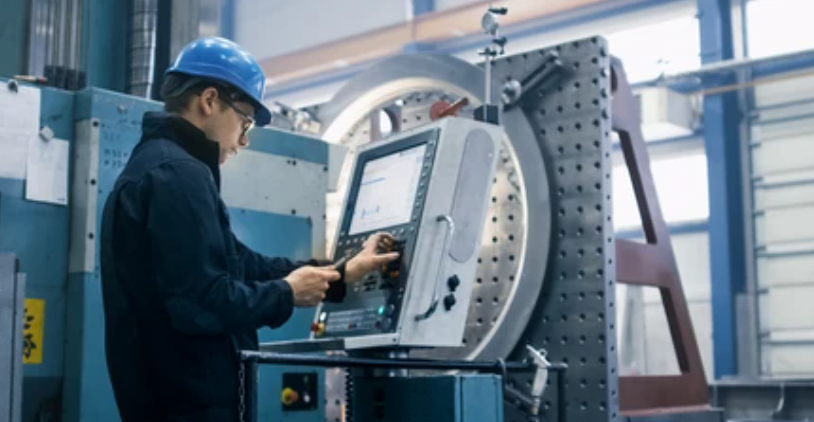

After that, put the material on the worktable. Aluminum, wood, plastic, or steel are some of the materials it might use. Make sure the screw is nice and tight so nothing can move.
You now get the appropriate cutting tool and put it into the machine. It depends on the project and the materials being used, and which tools are needed. Getting good results depends on how accurately you set up, just as much as on the software itself.
He or she lines up the tool with a zero point. The position from which the machine has started is now its reference point. After that, every movement by the competitor is kept under observation.
When things are ready, you can start pressing the start button. As soon as you press start, the machine starts going through the G-code. Motors, spindle, and drives get into operation.
You will not have to get involved as the process goes on. Speed, depth, a nd direction are being checked by the system. All of the movements in a robot are controlled by servo motors.
Most CNC machines are able to move on three axes or more. More axes lead to a more complex result. A number of systems today use 5+ axes to provide high precision.
As the process happens, sensors monitor all of the equipment. Devices check for heat, resistance, or wear on the tools. If there’s an error, the system hits the brakes or tells you something is wrong.
When the machining job is done, you check the part. Some kinds of manufacturing use CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines). They check all the sizes and how much the pieces can differ from the plan.
After that, finishing tasks like deburring, polishing, or cleaning are done. The choice is affected by the selected material and specs. When this is done, your part is set for shipment.
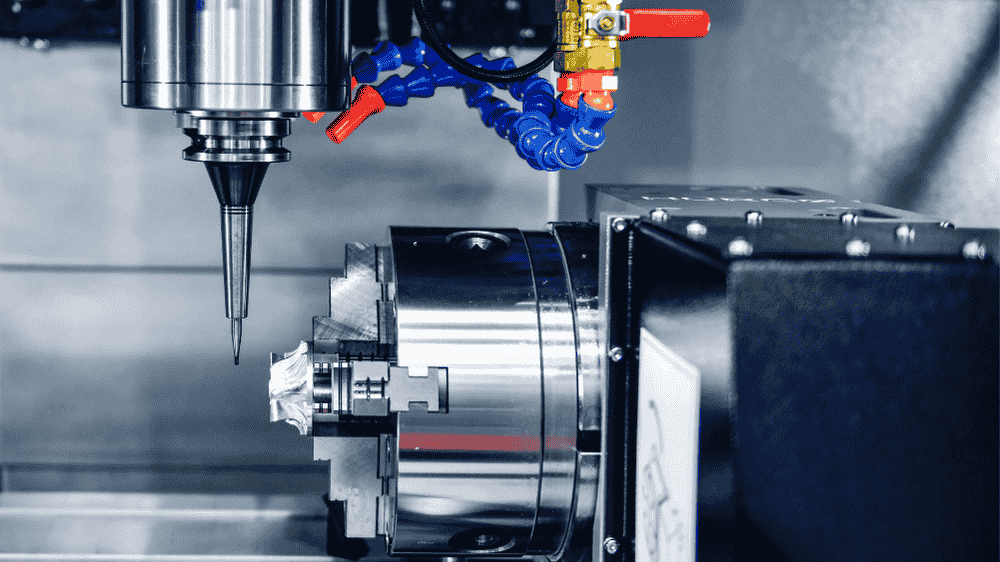
You’ll see these in nearly every machine shop. CNC milling machines cut and shape solid materials with rotating tools. They work across three, four, or even five axes.
You upload the design, and the spindle does the rest. It drills, slots, or contours parts with micrometer precision. From aerospace to prosthetics, accuracy is non-negotiable here.
In 2024, milling machines made up 35% of CNC sales. Manufacturers lean on them for prototyping and high-precision tasks. You can’t build engines or molds without them.
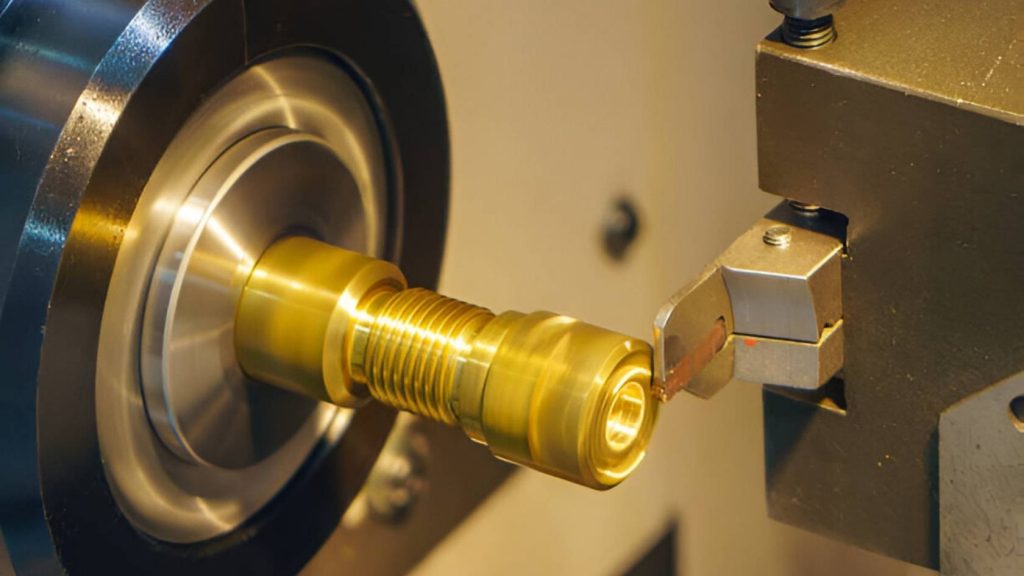
When symmetry plays a prominent role in your part, you rely on CNC lathes. Machines such as these rotate the part being made while a fixed tool works on it. It can easily be used to create shafts, pins, and pulleys.
Mill machines cut on multiple axes, whereas lathes only cut on one axis. You are still able to set the speed of the feed and the speed of the spindle. Precision turning requires fewer post-processing steps.
About 25% of precision parts are now machined using CNC lathes. Many industries, for example, oil and gas, turn to them for making cylindrical objects. Production runs? They are always doing their job with no interruptions.
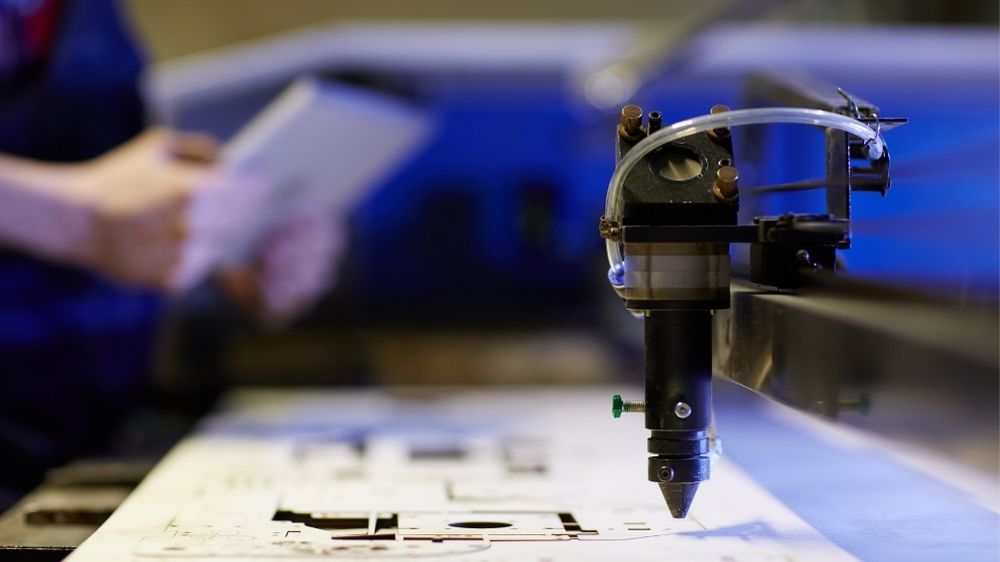

You can do a cut without being in contact with the person. A high-powered laser is used by CNC laser machines. Materials can be melted, burned, or vaporized without leaving a mess.
They are very capable of cutting sheet metals and thin composites. You are able to change the intensity, the speed, and the track of the beam. It results in less waste being produced waste and the knives have no rough edges.
Worldwide demand for oil went up by 12% in 2023. Electronics, jewelry, and automobiles are common places for you to see these sheets. Their key is getting things done smoothly and calmly..
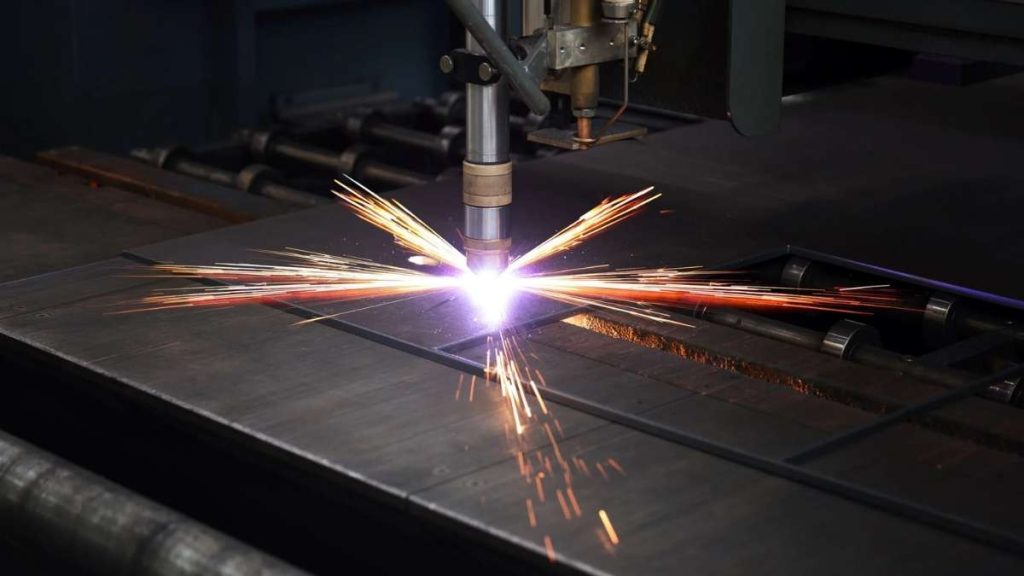

When you need speed and power, plasma works best. These machines cut through conductive metals using ionized gas. The torch reaches 20,000°C or more.
You position the material, set the path, and fire. Plasma CNCs slice steel, aluminum, and copper in seconds. They shine in large-scale metalwork projects.
Heavy industries love them for structural cuts. In shipbuilding and fabrication, plasma saves time. Compared to lasers, they handle thicker stock with ease.
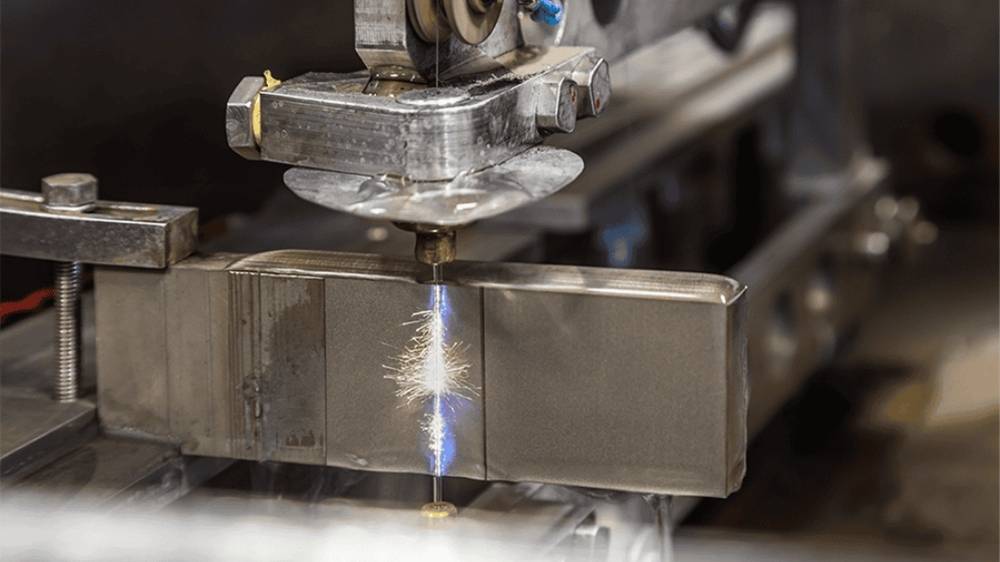

EDM uses sparks to cut, not blades or beams. You submerge the part in dielectric fluid, then apply electric discharges. It’s slow but ultra-precise.
You won’t see these in casual shops. EDM is for hardened metals and complex cavities. Molds, dies, and turbine parts rely on this tech.
In 2024, EDM machines served over 80% of tool-and-die shops. Aerospace and medical sectors count on them for micro-scale detail. You choose EDM when others fail.
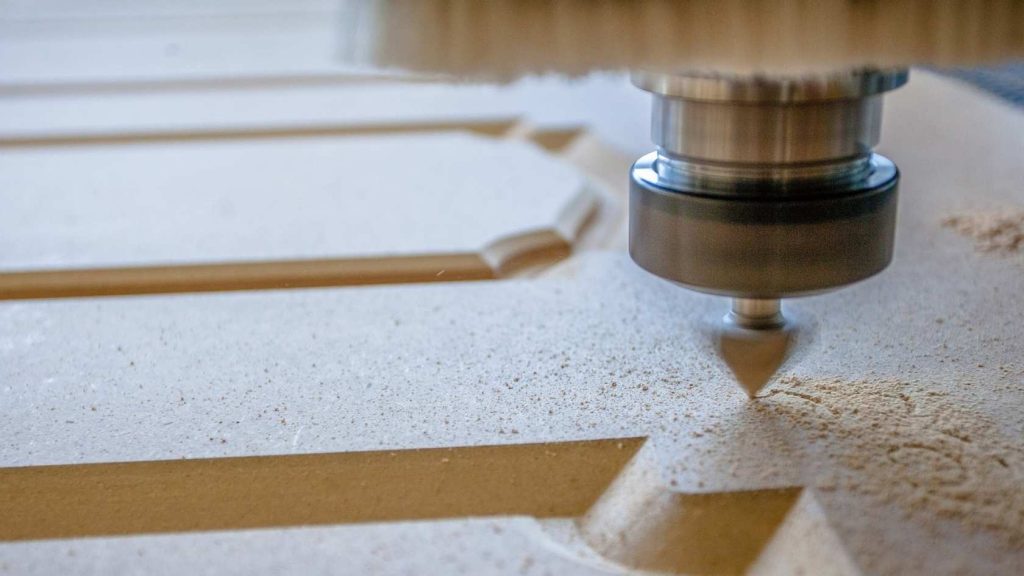

You’ll find routers in both factories and garages. CNC routers carve soft materials like wood, plastic, and foam. They’re perfect for panels, signs, and furniture.
The machine moves quickly over large surfaces. You upload the file, and it routes the pattern cleanly. Dust collection is a must with this one.
Routers own the woodworking automation space. In 2023, they drove 40% of small-shop CNC adoption. They blend speed, detail, and lower costs effortlessly.
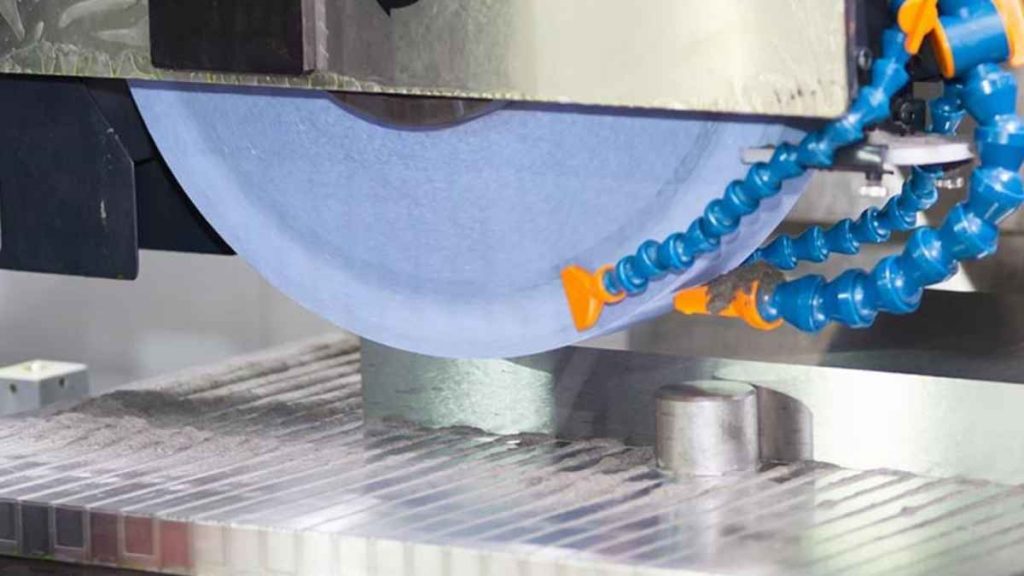

You turn to grinding when finish matters most. CNC grinding machines remove tiny amounts of material. They shape and polish surfaces to extreme precision.
These machines use rotating abrasive wheels. You control the pressure, speed, and feed. That ensures a consistent, smooth finish on every pass.
Grinding dominates tool, bearing, and gear production. In 2024, it held 15% of the precision machining market. You’ll find them in aerospace, defense, and medical device lines.
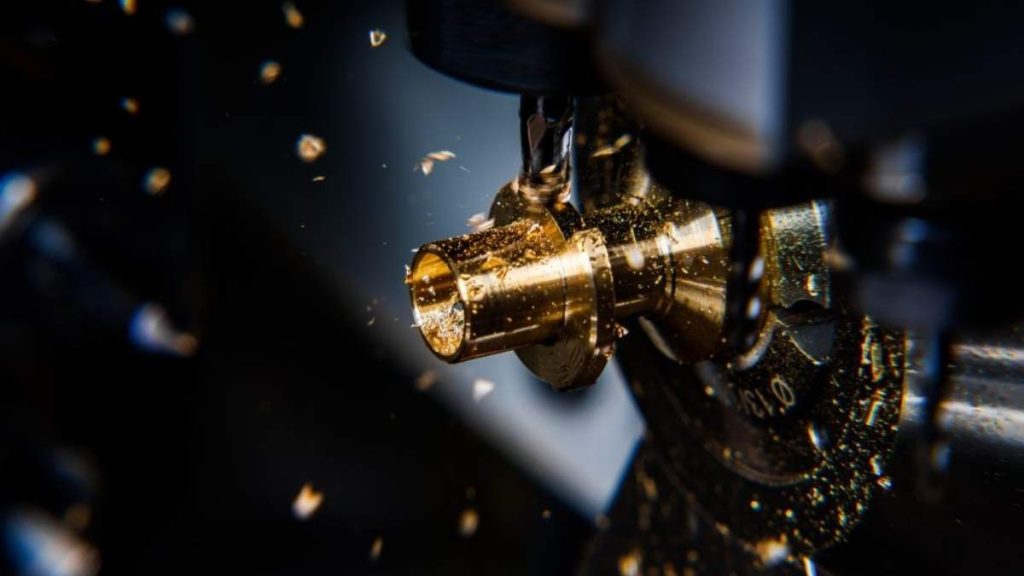

You need drilling to create clean, accurate holes. CNC drilling machines push bits into materials vertically. They drill thousands of holes with identical spacing and depth.
You load the material, align the bit, and go. From circuit boards to engine blocks, they handle mass runs. Multi-spindle options boost output.
Drilling now powers over 20% of high-speed CNC tasks. Electronics, construction, and aerospace all depend on it. The margin for misalignment? Practically zero.
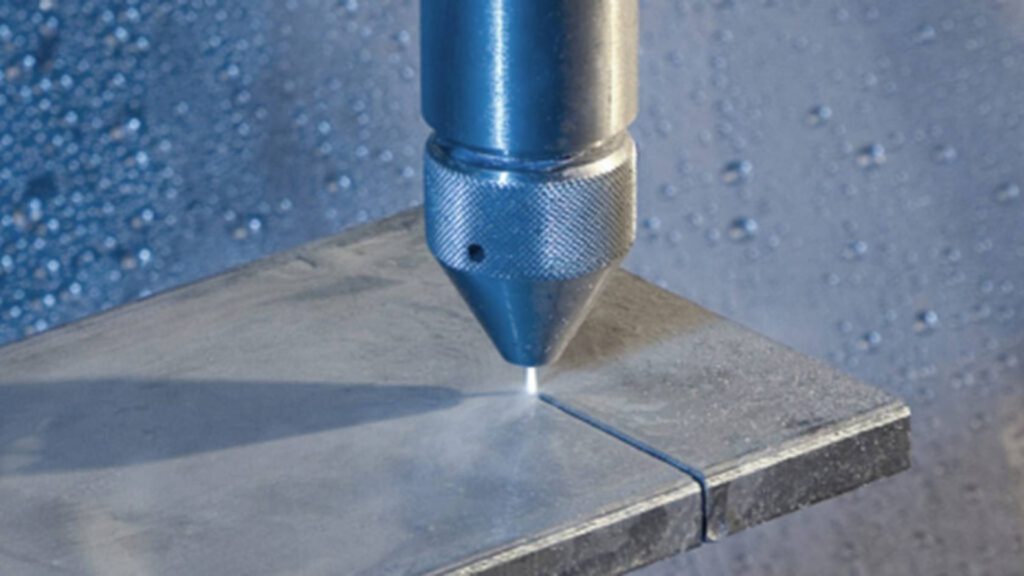

You cut with water, not heat, in this case. CNC waterjet machines use high-pressure streams mixed with abrasives. They slice stone, metal, glass, and rubber with ease.
Waterjets keep material cool during cuts. That’s critical for thermally sensitive parts. You avoid warping and discoloration entirely.
By 2024, waterjet tech will have expanded into aerospace and art. It’s ideal for detailed cuts on thick, layered stock. When lasers can’t cut it, water can.
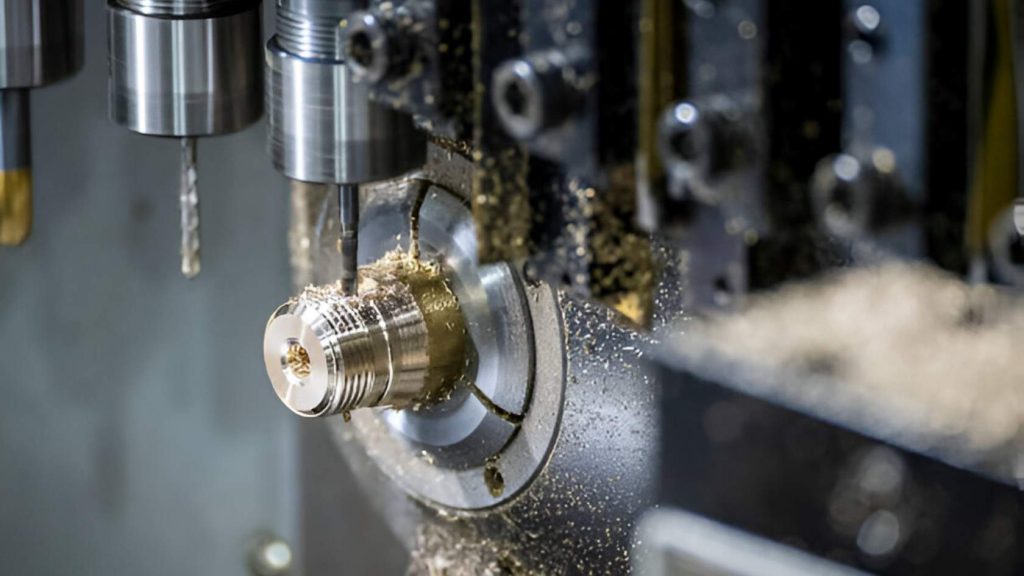

Swiss lathes can make very precise pieces for small jobs. You move bar stock through a guide bushing. The tool gets very close to the point of support.
The finish becomes smoother and quieter because of this. Such fasteners are used for medical implants, watch components, and aerospace fasteners. Tolerances are normally very precise.
In 2024, there was a 10% increase in the number of machines used. The fact that they have complex, small parts makes them irreplaceable. People pick Swiss because standard lathes won’t do the job.
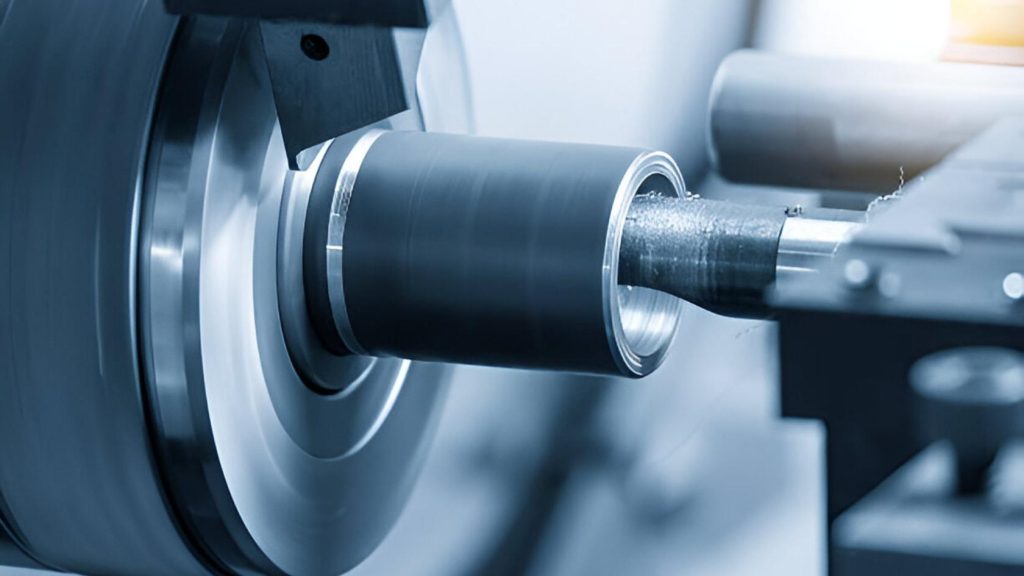
CNC boring makes holes bigger than they were originally with great accuracy. It adjusts the interior surfaces of the cylinders, gearbox box and machine body. The internal surfaces are clean, and you can get the diameters you want.
While drilling can be done in many ways, boring always needs stability and deep penetration. The spindle is always in the center as the tool cuts the item. It mostly depends on controlling the internal geometry.
Turbines, engine blocks, and similar products are often bored in heavy industries. They are designed to process very heavy and powerful workpieces. Boring happens after all the other steps in precision manufacturing.
You don’t just buy a CNC machine—you match it. The right one depends on your work, budget, and precision needs. Each machine serves a unique industrial role.
Choosing the wrong leads to wasted money and delays. Let’s break down how to make the right call—step by step.
First, decide on the material you want to cut. This makes the number of options go down very quickly. Soft materials? Use routers or waterjets for the job.
Have to work on materials that are hard metallic surfaces? Mills, lathes, and EDMs are good options to look at. Plasma and lasers can be used on metal, too. What you are making will decide what machine you need.
Titanium, which heats up easily, should be cut carefully with precision. This is when having an EDM or multi-axis mill is very useful. You pick materials based on their strength and the reaction they have.
Basic cuts can be made with basic machines. If what you need is curves, angles, or moves in multiple axes, choose a 4 or 5-axis machine.
Milling does a good job with the contours and 3D forms of a product. Lathes are excellent at making symmetrical items. Swiss-type fonts are great for making tiny and detailed things.
Don’t overbuy. Lay out the machine according to the shape of the part. When pieces are complex, machines with great predictability and accurate ranges are important.
Are you making only one part or a large number of them? Prototypes need to be flexible, which is why milling or router tools are recommended.
When making a lot of parts, most machinists prefer lathes and Swiss-type machines. They are very fast, reliable, and suitable for working at any time of day.
Wood and composites are routed in batch runs with CNC routers. Even though EDM requires much time for each part, it is important for making highly detailed elements in small numbers. Set the speed of the machine to match how fast the products are being produced.
Yet another way to look at it is that price can make a big difference. It costs more to buy a multi-axis machine. Therefore, EDM or Swiss machining is very precise as well.
Basic operations can be done with routers or basic mills if you run a small business. Increasingly large operations will use automation for tool changing, plus coolant systems and special software.
Remember that your manufacturing process needs upkeep, like tooling, power, and fixing problems. Include training for operators and help using digital features. A solid budget is important to see the effects later on.
You’ve seen the options. Now let’s talk fit. The best CNC machine depends entirely on your material, part design, and scale.
You don’t need the most expensive machine. You need the most appropriate one. Here's how to choose smartly based on real project needs.
Use CNC Milling or EDM machines. If your part needs tight tolerances, 3D contouring, or custom cavity shapes, start here.
EDM works best for hardened metals and complex geometries. Milling machines offer flexibility for parts with variable features. These dominate aerospace and medical work.
Go with CNC Lathes or Swiss-Type Lathes. They spin the part while shaping it. If you're making shafts, pins, or connectors, this is your zone.
Swiss lathes are your choice for extremely small, precise parts. Think watch gears or surgical screws. They’re the champions of miniature detail.
Choose CNC Laser, Plasma, or Waterjet machines. They cut flat stock fast and clean. Use lasers for thin metal, plasma for thick steel, and waterjets for heat-sensitive material.
If you want zero heat distortion, pick waterjet. If speed and power matter, plasma wins. Lasers offer an unbeatable edge quality on thin material.
You need a CNC Router. It’s fast, cost-efficient, and easy to use. Furniture makers, sign shops, and hobbyists all rely on them.
Routers handle large sheets and complex curves well. They’re the go-to for decorative or structural designs in soft materials.
Initial holes are made by drills; the refining is done by bores. The part’s inside diameter has to be exact if this is discussed at the quote stage.
Circuit boards? Pick fast drilling units. Engine blocks? You should go for boring machines. Precise depth and how well the structure is aligned are the key.
You’ve now explored the full CNC machine landscape. From milling to plasma, each type serves a distinct role. And each one can make—break our project.Don’t buy on instinct. Choose based on precision, material, and output needs. CNC success comes from smart alignment, not flashy specs.
The right machine boosts speed, lowers waste, and guarantees repeatability. That’s why industries—from aerospace to art studios—trust CNC for mission-critical tasks.So here’s your next move: match your project’s demands to the machine’s core strength. When you do that, you don’t just machine a part—you engineer results.
